The emerging role of cuproptosis in spinal cord injury
- PMID: 40589743
- PMCID: PMC12206656
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1595852
The emerging role of cuproptosis in spinal cord injury
Abstract
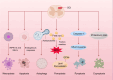
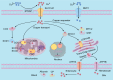
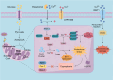
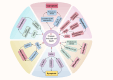
Copper is a vital trace element integral to numerous biological processes, including iron metabolism, neurotransmitter synthesis, mitochondrial respiration, oxidative stress regulation, and energy production. However, disturbances in copper metabolism can result in pathological conditions, including cuproptosis-a newly recognized form of programmed cell death (PCD) marked by copper accumulation and the disruption of copper-dependent metabolic pathways. Cuproptosis has been associated with various diseases, such as cancer, metabolic disorders and neurodegenerative disorders. In the context of spinal cord injury (SCI), multiple pathological mechanisms, including oxidative stress, inflammation, and PCD could impact the patient's prognosis with SCI. This review seeks to elucidate the pathophysiological underpinnings of SCI, the mechanisms and biological significance of copper homeostasis and the role of cuproptosis in SCI.
Keywords: copper homeostasis; cuproptosis; programmed cell death; reactive oxygen species; spinal cord injury.
Copyright © 2025 Xu, Hu, Zhou, Deng, Zhu and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cuproptosis: a novel therapeutic mechanism in lung cancer.Cancer Cell Int. 2025 Jun 24;25(1):231. doi: 10.1186/s12935-025-03864-1. Cancer Cell Int. 2025. PMID: 40555995 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cuproptosis: Mechanisms, biological significance, and advances in disease treatment-A systematic review.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024 Sep;30(9):e70039. doi: 10.1111/cns.70039. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024. PMID: 39267265 Free PMC article.
-
From ferroptosis to cuproptosis, and calcicoptosis, to find more novel metals-mediated distinct form of regulated cell death.Apoptosis. 2024 Jun;29(5-6):586-604. doi: 10.1007/s10495-023-01927-0. Epub 2024 Feb 7. Apoptosis. 2024. PMID: 38324163 Review.
-
Merestinib inhibits cuproptosis by targeting NRF2 to alleviate acute liver injury.Free Radic Biol Med. 2025 Mar 1;229:68-81. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2025.01.029. Epub 2025 Jan 15. Free Radic Biol Med. 2025. PMID: 39824447
-
MAPK signaling pathway in spinal cord injury: Mechanisms and therapeutic potential.Exp Neurol. 2025 Jan;383:115043. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2024.115043. Epub 2024 Nov 8. Exp Neurol. 2025. PMID: 39522804 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

