Skin pedicle expansion technique in dorsal nerve fascial Island flap: enhancing viability in repairing digital soft tissue defects
- PMID: 40590961
- PMCID: PMC12214020
- DOI: 10.1007/s00423-025-03800-x
Skin pedicle expansion technique in dorsal nerve fascial Island flap: enhancing viability in repairing digital soft tissue defects
Abstract
Purpose: Various flap techniques have been developed for injuries to the middle and distal phalanges, with the dorsal nerve fascial island (DNFI) flap offering distinct advantages. We aimed to elucidate the process of skin pedicle expansion (SPE) during DNFI flap transplantation and its effectiveness in relieving pressure on the fascial pedicle.
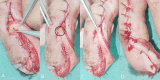
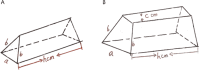
Methods: Ninety-two patients with soft tissue defects in the middle and distal phalanges were treated using a DNFI flap from February 2008 to August 2023. Eighty-three patients underwent SPE. The SPE technique involves creating a 3- to 4-mm wide skin strip on the surface of the fascial tissue, which contains a small arterial-venous system along with dorsal nerves, enabling the flap to remain viable. The fascial pedicle reaches the defect area via an incision (the skin channel). The skin pedicle transforms the shape of the channel from triangular to trapezoidal, thereby increasing its capacity. After flap rotation and suturing, the design reduced the pressure of the channel on the fascial pedicle. Theoretically, this should facilitate smoother arterial and venous circulation within the flap, thereby improving survival rates.
Results: All 83 flaps treated using the SPE technique survived. However, one patient experienced flap necrosis, and two patients had partial necrosis in the non-SPE group, with only six patients presenting satisfactory survival outcomes.
Conclusions: SPE may improve the viability of DNFI flaps by alleviating pressure on the fascial pedicle, ensuring adequate blood flow, and enhancing flap viability. SPE has the potential to be a valuable technique in hand-repair surgery.
Level of evidence: Level 4 according to the Oxford Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine (OCEBM).
Keywords: Compression; Dorsal digital nerve; Fascia; Finger; Flap; Skin pedicle expansion.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was approved by the ethics committee of our institution. The skin pedicle technique and dorsal nerve fascial island (DNFI) flap were approved for clinical use by the authors’ institution. All procedures involving human participants performed in this study were in accordance with the ethics standards of the institutional and national research committee and the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants in this study and is stored in the Department of Medical Records at our institution. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Consent to publish: Not applicable. Authors’ information: XW, Deputy Director, Department of Hand and Foot Surgery, The Third Hospital of Xiamen, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xiamen University (Tongan Branch), Xiamen, Fujian, China. Academic Societies:: Member, Chinese Medical Association Fujian Branch for Microscopic Surgery. Member, Chinese Medical Association Fujian Branch for Tissue Regeneration and Repair. Member, Xiamen Association of the Integration of Traditional and Western Medicine for Trauma. Expert Panel Member, Chinese Medical Association Xiamen Branch for Medical Accident and Medical Damage Identification. Clinical Specializations:: Wound Repair. Foot and Hand Diseases. Nerve and Vessel Repair.
Figures







References
-
- Liu QZ, Sun HB, Cai SY et al (2017) Clinical analysis of hand trauma with skin and soft tissue defects. Chin J Hand Surg 33:297–299. 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1005-054X.2017.04.022 - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

