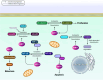
SIRT1 as a masterful reciprocal regulator of molecular mechanisms and signaling pathways involved in tumor growth and expansion
- PMID: 40591009
- PMCID: PMC12213863
- DOI: 10.1007/s10238-025-01759-z
SIRT1 as a masterful reciprocal regulator of molecular mechanisms and signaling pathways involved in tumor growth and expansion
Abstract
Sirtuin 1, which is more commonly identified as SIRT1, is a well-recognized NAD+-dependent histone and/or protein deacetylase that operates a wide range of cellular and molecular mechanisms involved in carcinogenic processes. SIRT1 not only regulates the primary mechanisms involved in tumorigenesis but also is responsible for controlling other processes, such as cell migration and metastasis, autophagy, and apoptotic flux, as well as chemotherapeutic resistance. It is well established that SIRT1 works at the upstream of signal transduction pathways, such as p53 signaling, together with FOXO mechanism, as well as the others. Indeed, SIRT1 by its deacetylase activity deacetylates different molecules in those signaling pathways and mostly causes a kind of blockade in the signaling of interest. Nonetheless, many aspects of SIRT1-cancer relationship are ambiguous, and more experiments should be performed for further uncovering of the concept. In the current review, we first highlight the major regulators of SIRT1 in cancer and then underscore key signal transduction pathways regulated by SIRT1. In the following, the role of SIRT1 will be discussed in tumor progression, from tumorigenesis to chemotherapeutic resistance, and at last, the contribution of SIRT1 to human cancers will be exemplified by some studies conducted in the field.
Keywords: Carcinogenesis; Drug resistance; Neoplasm; Signal transduction; Sirtuin 1.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics approval: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
ADNP dysregulates methylation and mitochondrial gene expression in the cerebellum of a Helsmoortel-Van der Aa syndrome autopsy case.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2024 Apr 18;12(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s40478-024-01743-w. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2024. PMID: 38637827 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Chen C, Zhou M, Ge Y, Wang X. SIRT1 and aging related signaling pathways. Mech Ageing Dev. 2020;187: 111215. 10.1016/j.mad.2020.111215. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous