Research trends and visualization analysis of autoimmune disease-related liver cancer from 2004 to 2024: a bibliometric study
- PMID: 40591043
- PMCID: PMC12214184
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-025-03042-9
Research trends and visualization analysis of autoimmune disease-related liver cancer from 2004 to 2024: a bibliometric study
Abstract
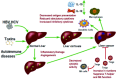
Background: Despite the rapid increase in scientific research output related to autoimmune disease-associated liver cancer (ADRLC) in recent years, there is currently a lack of a comprehensive and objective grasp of the cutting-edge progress and future research directions in this research field.
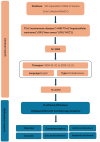
Methods: A comprehensive bibliometric analysis of ADRLC literature was conducted using Biblioshiny, VOSviewer, Scimago Graphica, CiteSpace, and Microsoft Office Excel (Version 2022). Data were extracted from the Web of Science Core Collection (2004-2024).
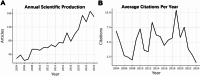
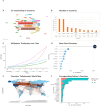
Results: A total of 1,672 ADRLC papers published from 2004 to 2024 were included. The number of global publications increased steadily, peaking in 2023. The United States had the most publications and citations, followed closely by China and Japan. The WORLD JOURNAL OF GASTROENTEROLOGY published the most articles. High-frequency keywords included "hepatocellular carcinom", "cancer", and "disease" six major research clusters were identified, with "natural history" having the strongest burst impact from 2004 to 2024. Recent trends included "immunotherapy" and "cancer" (2021-2024). Cutting-edge research directions were "immunotherapy" and "immune checkpoint inhibitors".
Conclusion: This study reveals the research directions and trends of ADRLC. The research on ADRLC is increasing globally, with significant contributions from China and the United States. Strengthening research on pathogenesis, early prevention, and individualized treatment of ADRLC is needed. Immunotherapy shows great potential in treating ADRLC and has become a current research hotspot.
Keywords: Autoimmune diseases; Bibliometrics; Immune checkpoint inhibitors; Immunotherapy; Liver cancer.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics and consent to Participate: Not applicable. Consent to publish: All authors agree to the publication of this article. Clinical trial number: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Research status, hotspots and perspectives of artificial intelligence applied to pain management: a bibliometric and visual analysis.Updates Surg. 2025 Jun 28. doi: 10.1007/s13304-025-02296-w. Online ahead of print. Updates Surg. 2025. PMID: 40580377
-
Bibliometric and visualized analysis of global distribution and research frontiers in tumor immune escape.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 5;16:1586120. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1586120. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40539064 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Global Analysis of Future Trends in Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Veterinary Medicine.Vet Med Sci. 2025 May;11(3):e70258. doi: 10.1002/vms3.70258. Vet Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40145983 Free PMC article.
-
A bibliometric review and visualization of research on myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in patients with diabetes mellitus from 2004 to 2024.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 May 30;104(22):e42707. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000042707. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40441190 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tracing inflammasomes in Alzheimer's: insights from bibliometric analysis.Front Neurol. 2025 Jun 5;16:1540083. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1540083. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40538660 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang X, Yang L, Liu S, Cao LL, Wang N, Li HC, Ji JF. [Interpretation on the report of global cancer statistics 2022]. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2024;46(7):710–21. - PubMed
-
- Li YK, Wu S, Wu YS, Zhang WH, Wang Y, Li YH, Kang Q, Huang SQ, Zheng K, Jiang GM, et al. Portal venous and hepatic arterial coefficients predict Post-Hepatectomy overall and Recurrence-Free survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective study. J Hepatocell Carcino. 2024;11:1389–402. - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
