Cellular and molecular mechanisms of arenobufagin in cancer therapy: a systematic review
- PMID: 40591087
- PMCID: PMC12214120
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-025-03052-7
Cellular and molecular mechanisms of arenobufagin in cancer therapy: a systematic review
Abstract
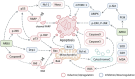
The search for effective and safe therapeutic options is the goal of clinical treatment for cancer patients. In recent years, natural products have received increasing attention in order to develop new drugs with good antitumor effects and fewer side effects. Arenobufagin (ARBU), an important active ingredient extracted from Toad venom, has been shown to exhibit anti-cancer effects in basic research. Studies have revealed that ARBU has a wide range of potent biological activities and plays an important role as an anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant, anti-viral, and for the treatment of cardiac insufficiency. ARBU has shown promising anti-cancer activity in preclinical research. Therefore, it has attracted increasing attention from researchers. In this paper, its antitumor effects were reviewed in terms of cell cycle arrest, induction of cell apoptosis and autophagy, improvement of immunity, inhibition of proliferation, angiogenesis, invasion and metastasis. In addition, the safety and toxicity of the compound were further discussed. Follow-up experiments, especially clinical trials, are needed in order to elucidate the benefits and adverse effects of ARBU on cancer patients.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Apoptosis; Arenobufagin; Cancer; Metastasis; Molecular mechanisms.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Consent for publication: All authors have agreed to publish this manuscript. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Antidepressants for pain management in adults with chronic pain: a network meta-analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Oct;28(62):1-155. doi: 10.3310/MKRT2948. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39367772 Free PMC article.
-
Etanercept and infliximab for the treatment of psoriatic arthritis: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(31):iii-iv, xiii-xvi, 1-239. doi: 10.3310/hta10310. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16948890
References
-
- Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74(3):229–63. 10.3322/caac.21834. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D. Hallmarks of cancer: new dimensions. Cancer Discov. 2022;12(1):31–46. 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-21-1059. - PubMed
-
- Lalla RV, Brennan MT, Gordon SM, Sonis ST, Rosenthal DI, Keefe DM. Oral mucositis due to high-dose chemotherapy and/or head and neck radiation therapy. J Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 2019. 10.1093/jncimonographs/lgz011. - PubMed
-
- Wall ME. Camptothecin and taxol: discovery to clinic. Med Res Rev. 1998;18(5):299–314.. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
