PDS5B positively regulates PTEN by binding to YTHDC1 to inhibit the malignant progression of endometrial carcinoma
- PMID: 40591192
- PMCID: PMC12214172
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-025-03021-0
PDS5B positively regulates PTEN by binding to YTHDC1 to inhibit the malignant progression of endometrial carcinoma
Abstract
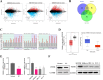
Background: Endometrial carcinoma (EC) is a common gynecological malignancy with a complex pathogenesis. PDS5B is revealed to be dysregulated and play critical roles in multiple cancers, while its role in EC remains largely unknown. The aim of this study was to explore the expression profile and biological function of the PDS5B in EC.
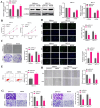
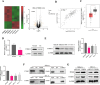
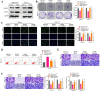
Methods: In this study, differential gene expression analysis in EC was performed using public databases and relevant analytical tools. The expression of PDS5B was verified by western blot and qRT-PCR in cell and tissue samples. The effects of PDS5B overexpression on EC cell proliferation, invasion and apoptosis, as well as the interaction of PDS5B with YTHDC1 and the regulation of PTEN stability were further explored by in vitro experiments. The effects of PDS5B on tumorigenesis and metastasis were explored using in vivo models.
Results: PDS5B was down-regulated in EC, and overexpression of PDS5B significantly inhibited cell growth, and promoted apoptosis. In vitro results revealed that PDS5B interacted with YTHDC1 in EC cells and YTHDC1 regulated PTEN expression and stability via m6A modification, affecting the biological behavior of EC cells. In in vivo nude mouse models, overexpression of PDS5B significantly inhibited EC tumor development and metastasis in nude mice.
Conclusions: PDS5B interacts with YTHDC1 and further regulates PTEN in endometrial cancer cells, thereby inhibiting the malignant development of the tumor. These findings indicate the potential part of PDS5B in the development of EC and provide new molecular targets for the treatment of EC.
Keywords: Endometrial carcinoma; M6A; PDS5B; PTEN; YTHDC1.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was performed according to the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki, and was approved by the Joint Ethics Committee of the Ministry of Health. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study. This study was approved by the Laboratory Animal Ethics Committee of Changzhou Geriatric Hospital Affiliated to Soochow University, Changzhou No. 7 People’s Hospital, and complied with the rules of Declaration of Helsinki principles. The maximal tumor size permitted by the ethics committee was 1000 mm3 and the maximal tumor burden was not exceeded in this study. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
