Experts' consensus on the management and treatment of individuals with X-linked hypophosphatemia across lifespan
- PMID: 40591205
- PMCID: PMC12518444
- DOI: 10.1007/s40618-025-02611-7
Experts' consensus on the management and treatment of individuals with X-linked hypophosphatemia across lifespan
Erratum in
-
Correction: Experts' consensus on the management and treatment of individuals with X-linked hypophosphatemia across lifespan.J Endocrinol Invest. 2025 Oct 8. doi: 10.1007/s40618-025-02703-4. Online ahead of print. J Endocrinol Invest. 2025. PMID: 41060522 No abstract available.
Abstract
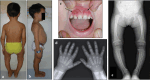
Purpose: X-linked hypophosphatemia (XLH) is a rare hereditary skeletal disorder that may be very disabling and significantly impacting the quality of life throughout the lifespan. The aim of this document was to inform stakeholders about the lifelong impact, management, and treatment of individuals with XLH, especially focusing on the new therapeutic approach with burosumab.
Methods: From October 2023 to April 2024, a multidisciplinary working group of Italian experts on bone and mineral metabolism convened periodic online meetings. Statements were formulated identifying the most relevant studies, including randomized controlled trials, international guidelines based on GRADE criteria, and systematic reviews, and the experts' opinions.
Results: The panel of experts provided "consensus statements" on the clinical management of individuals with XLH across lifespan. Five main issues were identified: (1) clinical and biochemical diagnosis of individuals with XLH and monitoring of the progression of the disease; (2) effects of conventional treatment with phosphate supplements and active vitamin D metabolites; (3) effects of the treatment with burosumab; (4) multidisciplinary approach and management of individuals with XLH; (5) consensus statement for transition from pediatric to adult care in individuals with XLH.
Conclusion: Individuals with XLH often experience unmet needs throughout life; a multidisciplinary approach involving different specialists, is recommended. The new treatment with burosumab can provide an effective and safety therapeutic option in reducing the burden of the disease in both children and adults. Therefore, awareness about the XLH disease should be increased among stakeholders. The criteria and reimbursement policies of burosumab should be revised.
Keywords: Burosumab; Conventional treatment; FGF23; Osteomalacia; Rickets; XLH.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: All Authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Beck-Nielsen SS, Brock-Jacobsen B, Gram J, Brixen K, Jensen TK (2009) Incidence and prevalence of nutritional and hereditary rickets in Southern Denmark. Eur J Endocrinol 160:491–497. 10.1530/EJE-08-0818 - PubMed
-
- Sandy JL, Nunez C, Wheeler BJ, Jefferies C, Morris A, Siafarikas A, Rodda CP, Simm P, Biggin A, Aum S, Elliot EJ, Munns CF (2023) Prevalence and characteristics of paediatric X-linked hypophosphataemia in Australia and New Zealand: results from the Australian and the New Zealand Paediatric Surveillance Units survey. Bone 173:116791. 10.1016/j.bone.2023.116791 - PubMed
-
- Crisafulli S, Ingrasciotta Y, Vitturi G, Fontana A, L’Abbate L, Alessi Y, Ferraù F, Cantarutti L, Lazzerini D, Cannavò S, Trifirò G (2024) Epidemiological analysis to identify predictors of X-linked hypophosphatemia (XLH) diagnosis in an Italian pediatric population: the EPIX project. Endocrine 85:894–905. 10.1007/s12020-024-03793-5 - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

