Identification and characterization of nine PAT1 genes subfamily in Medicago edgeworthii
- PMID: 40592482
- PMCID: PMC12218496
- DOI: 10.1080/15592324.2025.2527380
Identification and characterization of nine PAT1 genes subfamily in Medicago edgeworthii
Abstract
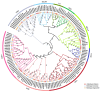
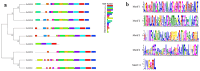
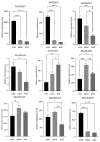
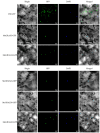
GRAS proteins represent a unique class of transcription factors that are exclusive to plants. Among the various subfamilies within the GRAS family, the phytochrome A signal transduction 1 (PAT1) subfamily is particularly prominent, given its multifaceted regulatory functions in phytochrome signaling pathways and stress response mechanisms, as well as its involvement in plant developmental processes. Despite the recognized importance of GRAS proteins, there are no studies to date that have characterized the GRAS gene family in Medicago edgeworthii. In this study, we performed a comprehensive genome-wide analysis of GRAS genes and identified nine genes belonging to the PAT1 subfamily in M. edgeworthii. Multiple sequence alignment of these proteins revealed the presence of a conserved C-terminal GRAS domain, alongside a highly variable N-terminal region. Additionally, we observed that members of the PAT1 subfamily were expressed in roots, stems, and leaves, indicating their broad involvement in the development of various tissues in M. edgeworthii. Furthermore, functional analysis indicated that PAT1 subfamily proteins in M. edgeworthii activated the expression of MeDOF3.4 gene, indicating that PAT1 subfamily proteins may be associated with the promotion of cell proliferation and graft fusion. In conclusion, this study provided the first comprehensive characterization of PAT1 subfamily genes in M. edgeworthii, establishing a foundation for future research on the functional roles of MeGRAS genes and providing a theoretical basis for the development of high-quality Medicago varieties.
Keywords: GRAS gene family; PAT1 subfamily gene; phylogenetic analysis; phytochrome.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures


References
-
- Di Laurenzio L, Wysocka-Diller J, Malamy JE, Pysh L, Helariutta Y, Freshour G, Hahn MG, Feldmann KA, Benfey PN. The SCARECROW gene regulates an asymmetric cell division that is essential for generating the radial organization of the Arabidopsis root. Cell. 1996;86(3):423–433. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80115-4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Peng J, Carol P, Fau -Richards DE, Richards de Fau - King KE, King Ke Fau - Cowling RJ, Cowling Rj Fau - Murphy GP, Murphy Gp Fau - Harberd NP. The Arabidopsis GAI gene defines a signaling pathway that negatively regulates gibberellin responses. Genes Devel. 1997;11(23):3194–3205. doi: 10.1101/gad.11.23.3194. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
