Klf5-adjacent super-enhancer functions as a 3D genome structure-dependent transcriptional driver to safeguard ESC identity
- PMID: 40592854
- PMCID: PMC12215363
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-60389-x
Klf5-adjacent super-enhancer functions as a 3D genome structure-dependent transcriptional driver to safeguard ESC identity
Abstract
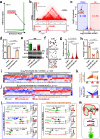
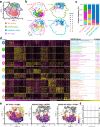
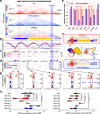
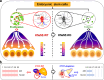
Cell-specific super-enhancers (SEs) and master transcription factors (TFs) dynamically remodel embryonic stem cell (ESC) fate, yet their regulatory interplay remains unclear. By integrating multi-omics data (H3K27ac, Hi-C, scRNA-seq) across ESC states, we identified SEs interacting with master TFs, exemplified by the Klf5-adjacent SE (K5aSE). K5aSE deletion impaired proliferation, differentiation, and Klf5 expression, partially rescued by KLF5 reintroduction. Despite phenotypic similarities between Klf5-KO and K5aSE-KO ESCs, scRNA-seq of embryoid bodies revealed distinct differentiation trajectories, suggesting K5aSE targets beyond Klf5. High-throughput 3D genome screening demonstrated K5aSE activates four distal genes via chromatin looping. CRISPRa-mediated activation of these targets rescued K5aSE-KO phenotypes and uncovered their regulatory roles. Furthermore, CTCF depletion disrupted topologically associated domains (TADs) near K5aSE, suppressing Klf5 and target gene expression, indicating CTCF-mediated TADs sustain K5aSE activity. Our study unveils a 3D genome-dependent mechanism by which SEs govern ESC identity through coordinated TF interaction and multi-gene regulation.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Stadhouders, R., Filion, G. J. & Graf, T. Transcription factors and 3D genome conformation in cell-fate decisions. Nature569, 345–354 (2019). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

