The relationship of the ratio of platelet distribution width to serum albumin with kidney disease progression in patients with hypertension
- PMID: 40593009
- PMCID: PMC12217693
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-05575-z
The relationship of the ratio of platelet distribution width to serum albumin with kidney disease progression in patients with hypertension
Abstract
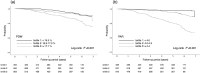
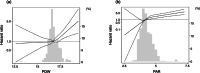
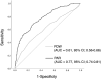
Platelet distribution width (PDW), which represents the heterogeneity of platelet size, can predict a poor prognosis in various populations. However, the PDW-to-serum albumin ratio (PAR) has not been evaluated in any disease population, and whether the PAR could be a prognostic marker in hypertension remains unknown. The relationship between the PAR and adverse outcomes was examined retrospectively using longitudinal data of 1,578 patients with hypertension from the Fukushima Cohort Study. Participants were categorized into tertiles by baseline PAR. The primary endpoint of the present study was a kidney event, defined as a combination of a 50% decline in eGFR from baseline and end-stage kidney disease requiring kidney replacement therapy. During the median follow-up period of 5.4 years, 146 patients had kidney events. The higher PAR group (tertile 3) showed an increased incidence of kidney events on Kaplan-Meier curve analysis. Compared with the lowest PAR tertile, the highest PAR tertile (tertile 3) showed a significantly higher risk of kidney events (adjusted hazard ratio 3.74, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.65-8.48). Similar relationships were observed for risks of all-cause death and cardiovascular events. The predictive value of the PAR for kidney events was superior to that of PDW alone. The areas under the curves for PDW and the PAR were 0.61 (95% CI 0.56-0.66) and 0.77 (95% CI 0.74-0.81), respectively (P < 0.001). The PAR could be a useful predictive marker of adverse outcomes in this population.
Keywords: Hypertension; Kidney; Observational study; Platelet distribution width; Prognosis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
-
Sertindole for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;2005(3):CD001715. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001715.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. PMID: 16034864 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of residual disease as a prognostic factor for survival in women with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer after primary surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 26;9(9):CD015048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015048.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36161421 Free PMC article.
-
Early referral strategies for management of people with markers of renal disease: a systematic review of the evidence of clinical effectiveness, cost-effectiveness and economic analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2010 Apr;14(21):1-184. doi: 10.3310/hta14210. Health Technol Assess. 2010. PMID: 20441712
-
Comparison of cellulose, modified cellulose and synthetic membranes in the haemodialysis of patients with end-stage renal disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001;(3):CD003234. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003234. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;(3):CD003234. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003234.pub2. PMID: 11687058 Updated.
References
-
- Vatankulu, M. A. et al. A new parameter predicting chronic total occlusion of coronary arteries: platelet distribution width. Angiology65, 60–64 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Rechciński, T. et al. Prognostic value of platelet indices after acute myocardial infarction treated with primary percutaneous coronary intervention. Cardiol. J.20, 491–498 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Osselaer, J. C., Jamart, J. & Scheiff, J. M. Platelet distribution width for differential diagnosis of thrombocytosis. Clin. Chem.43, 1072–1076 (1997). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

