Homocysteine promotes cardiomyocyte hypertrophy through inhibiting β-catenin/ FUNDC1 mediated mitophagy
- PMID: 40593088
- PMCID: PMC12214670
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-06772-6
Homocysteine promotes cardiomyocyte hypertrophy through inhibiting β-catenin/ FUNDC1 mediated mitophagy
Abstract
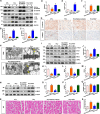
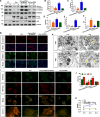
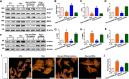
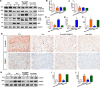
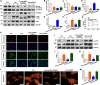
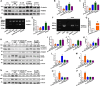
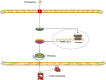
Homocysteine can cause damage to cardiomyocytes. However, Mitophagy is essential for preserving homeostasis in cardiomyocytes. So, we focused on investigating the impact of homocysteine on cardiomyocyte mitophagy and cardiac hypertrophy through the β-catenin/FUNDC1 pathway. Mice were administered water containing homocysteine (1.8 g/L) to induce hyperhomocysteinemia for 4 weeks. The overexpression of specific genes, including β-catenin and FUNDC1, were performed by gene delivery mediated with adeno-associated virus. In vitro, cardiomyocytes were exposed to homocysteine (1 mmol/L) and then transfected with plasmids to overexpress β-catenin and FUNDC1, respectively. The duration of cell experiments was 48 h. Western blotting was employed to assess the expression levels of β-catenin, active β-catenin, FUNDC1, LC3, p62, α-actin, and β-MHC. Immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescence techniques were applied to measure β-catenin and FUNDC1 in cardiomyocytes. Cell viability was assessed using a CCK-8 assay kit, and mitophagy was observed under transmission electron microscopy. The interaction between β-catenin protein and the promoter of the FUNDC1 gene was examined using ChIP assay and dual-luciferase reporter gene assay. Homocysteine inhibited β-catenin signaling and the FUNDC1-mediated mitophagy in the cardiomyocytes, simultaneously promoting cardiac hypertrophy in vitro and in vivo. Elevated β-catenin signaling promoted FUNDC1 expression, then restored the normal level of mitophagy, and consequently inhibited homocysteine-induced cardiac hypertrophy. Similarly, overexpression of FUNDC1 restored mitophagy and protected cardiomyocytes from hypertrophy. In addition, FUNDC1 served as a target gene of β-catenin. In summary, homocysteine induces cardiomyocyte hypertrophy by inhibiting β-catenin signaling and suppressing FUNDC1-mediated mitophagy.
Keywords: Cardiomyocyte hypertrophy; FUNDC1; Homocysteine; Mitophagy; β-catenin.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics approval: This study protocol was reviewed and approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of University of South China (Ethics approval number: USC2023XS087).
Figures
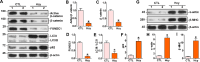
Similar articles
-
Homocysteine induces ferroptosis in cardiomyocytes by disrupting β-catenin/GPX4 pathway.PLoS One. 2025 Aug 6;20(8):e0329792. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0329792. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40768425 Free PMC article.
-
Homocysteine induces ferroptosis in renal tubular epithelial cells via β-catenin/GPX4 signaling pathway.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 4;15(1):23953. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-09221-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40615532 Free PMC article.
-
[Impact of tyrosine phosphorylation site mutation in FUNDC1 protein on mitophagy in H9c2 cardiomyocytes].Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2025 Jul;41(7):629-636. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40620120 Chinese.
-
Cordycepin Ameliorates Kainic Acid-Induced HT22 Cell Neurotoxicity by Activating GPR120-Mediated Mitophagy.Dev Neurobiol. 2025 Apr;85(2):e22961. doi: 10.1002/dneu.22961. Dev Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40007070 Review.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2021JJ40476/Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province
- 2022JJ30528/Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province
- 2021JJ40506/Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province
- 21B0414/Scientific Research Project of Hunan Provincial Department of Education
- C202303019182/Scientific Research Fund Project of Hunan Provincial Health Commission
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

