A small molecule enhances arrestin-3 binding to the β2-adrenergic receptor
- PMID: 40593109
- PMCID: PMC12214645
- DOI: 10.1038/s42004-025-01581-4
A small molecule enhances arrestin-3 binding to the β2-adrenergic receptor
Abstract
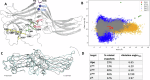
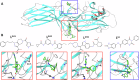
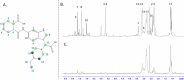
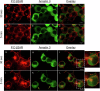
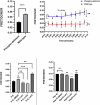
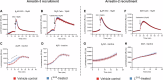
Excessive signaling by various GPCRs underlies a variety of human disorders. Suppression of GPCRs by "enhanced" arrestin mutants was proposed as therapy. We hypothesized that GPCR binding of endogenous arrestins can be increased by small molecules stabilizing pre-activated conformation. Using molecular dynamics, we identified potentially druggable pockets in pre-activated conformation of arrestin-3 and discovered a compound targeting one of these pockets. Saturation-transfer difference NMR data showed that the compound binds at the back loop of arrestin-3. FRET- and NanoBiT-based assays in living cells showed that the compound increased in-cell arrestin-3, but not arrestin-2, binding to basal β2-adrenergic receptor and its phosphorylation-deficient mutant, but not to muscarinic M2 receptor. These experiments demonstrated the feasibility of enhancing the binding of endogenous wild type arrestin-3 to GPCRs in a receptor-specific and arrestin-subtype selective manner.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Update of
-
A small molecule enhances arrestin-3 binding to the β2-adrenergic receptor.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Dec 13:2024.12.12.628161. doi: 10.1101/2024.12.12.628161. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Commun Chem. 2025 Jul 1;8(1):194. doi: 10.1038/s42004-025-01581-4. PMID: 39713392 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
A small molecule enhances arrestin-3 binding to the β2-adrenergic receptor.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Dec 13:2024.12.12.628161. doi: 10.1101/2024.12.12.628161. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Commun Chem. 2025 Jul 1;8(1):194. doi: 10.1038/s42004-025-01581-4. PMID: 39713392 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor-mediated phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase in HSY salivary ductal cells involves distinct signaling pathways.J Oral Biosci. 2024 Jun;66(2):447-455. doi: 10.1016/j.job.2024.02.002. Epub 2024 Feb 8. J Oral Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38336259
-
Comparison of cellulose, modified cellulose and synthetic membranes in the haemodialysis of patients with end-stage renal disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001;(3):CD003234. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003234. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;(3):CD003234. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003234.pub2. PMID: 11687058 Updated.
-
Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 19;10(10):CD012859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012859.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33075160 Free PMC article.
-
Inhaled corticosteroids with combination inhaled long-acting beta2-agonists and long-acting muscarinic antagonists for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Dec 6;12(12):CD011600. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011600.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 38054551 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lohse, M. J., Benovic, J. L., Codina, J., Caron, M. G. & Lefkowitz, R. J. β-arrestin: a protein that regulates β-adrenergic receptor function. Science248, 1547–1550 (1990). - PubMed
-
- Moore, C. A. C., Milano, S. K. & Benovic, J. L. Regulation of receptor trafficking by GRKs and arrestins. Annu. Rev. Physiol.69, 451–482 (2007). - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

