mRNA ratios of AR to ESR1 and PGR distinguish breast cancer subtypes based on public datasets and experimental models
- PMID: 40593140
- PMCID: PMC12216603
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-06856-3
mRNA ratios of AR to ESR1 and PGR distinguish breast cancer subtypes based on public datasets and experimental models
Abstract
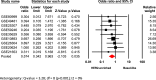
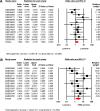
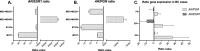
The role of the androgen receptor (AR) in breast cancer (BC) remains incompletely understood. Here, we conducted a meta-analysis of large-scale microarray transcriptomic datasets to evaluate whether the mRNA expression levels of the androgen receptor gene, relative to those of the estrogen receptor gene (AR/ESR1 ratio) and the progesterone receptor gene (AR/PGR ratio), can help differentiate BC tumor subtypes. Additionally, we used qRT-PCR assays to assess the mRNA levels of the AR/ESR1 and AR/PGR ratios in four cell lines representative of different BC subtypes (MCF7, BT474, MDA-MB453, and MDA-MB231), as well as in breast tissue from a small group of patients (11 cases) stratified by estrogen receptor (ER) status. Our results showed that higher AR gene expression relative to ESR1 and PGR (≥ 2.0 and ≥ 1.54, respectively) were associated with BC patients classified under the Luminal B and HER2-enriched subtypes. Positive values of AR/ESR1 and AR/PGR ratios were also observed in the ER-negative (ER-) cell line MDA-MB453, as well as in tumor tissue from ER- BC patients. Our findings confirm that higher or even positive AR/ESR1 and AR/PGR ratios may be associated with BC cases exhibiting more aggressive clinical and biological features, leading to a worse prognosis.
Keywords: Androgen receptor; Breast cancer; Estrogen receptor; Meta-analysis; Molecular subtypes; Progesterone receptor.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration. Competing interests: The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the study reported. Ethics approval: The use of samples from residual tissue was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Universidad del Rosario (ID Number of Ethics Committee: DVO005 956—CV1166). Approval for the use of samples from each of the patients, was obtained through written informed consent, which are stored physically in the archive of the Méderi hospital, where the samples were taken. Additionally, patient confidentiality and adherence to the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki were maintained.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Developmental expression patterns of gonadal hormone receptors in arcuate kisspeptin and GABA neurons of the postnatal female mouse.J Neuroendocrinol. 2025 Jan;37(1):e13477. doi: 10.1111/jne.13477. Epub 2024 Nov 28. J Neuroendocrinol. 2025. PMID: 39605295
-
PARP-1 as a novel target in endocrine-resistant breast cancer.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025 Jun 16;44(1):175. doi: 10.1186/s13046-025-03441-4. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40518539 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated proteomics and transcriptomics analysis reveals key regulatory genes between ER-positive/PR-positive and ER-positive/PR-negative breast cancer.BMC Cancer. 2025 Jul 1;25(1):1048. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-14451-y. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40597935 Free PMC article.
-
Androgen receptor and estrogen receptor variants in prostate and breast cancers.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2024 Jul;241:106522. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2024.106522. Epub 2024 Apr 17. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38641298 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
References
-
- Bray, F. et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin.74, 229–263 (2024). - PubMed
-
- Kim, J. et al. Global patterns and trends in breast cancer incidence and mortality across 185 countries. Nat. Med.31, 1154–1162 (2025). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

