Recent advances in CRISPR-based single-nucleotide fidelity diagnostics
- PMID: 40593148
- PMCID: PMC12219407
- DOI: 10.1038/s43856-025-00933-4
Recent advances in CRISPR-based single-nucleotide fidelity diagnostics
Abstract
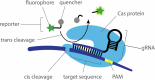
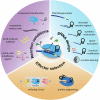
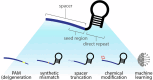
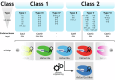
Accurate point-of-care (PoC) detection of single nucleotide variants (SNVs) can support rapid and cost-effective clinical decision-making in tasks such as diagnosing pathogenic genetic variants, identifying pathogen resistance, or tracing viral lineage differentiation. Traditional nucleic acid diagnostics involving PCR and sequencing lack PoC applicability. CRISPR-based diagnostics (CRISPRdx) offer the necessary operational simplicity and ability to integrate specific nucleic acid sequence detection with isothermal amplification. However, achieving single-nucleotide fidelity is not self-evident and often requires empirical optimization. This Review explores recent strategics aimed at refining CRISPRdx specificity for SNV detection including various ways of tactical guide RNA (gRNA) design, fine-tuned effector selection, and improved reaction conditions. While the approaches described here are functional and can be occasionally combined, they often require optimizations to support specific clinical aims. Looking ahead, leveraging computational and AI tools for gRNA design, and harnessing newly discovered CRISPR systems, will broaden applicability and improve precision detection of CRISPRdx in diverse clinical settings.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid molecular tests for tuberculosis and tuberculosis drug resistance: a qualitative evidence synthesis of recipient and provider views.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Apr 26;4(4):CD014877. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014877.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35470432 Free PMC article.
-
NIH Consensus Statement on Management of Hepatitis C: 2002.NIH Consens State Sci Statements. 2002 Jun 10-12;19(3):1-46. NIH Consens State Sci Statements. 2002. PMID: 14768714
-
Automated monitoring compared to standard care for the early detection of sepsis in critically ill patients.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jun 25;6(6):CD012404. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012404.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29938790 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid, point-of-care antigen tests for diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jul 22;7(7):CD013705. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013705.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35866452 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Precision Neuro-Oncology in Glioblastoma: AI-Guided CRISPR Editing and Real-Time Multi-Omics for Genomic Brain Surgery.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 30;26(15):7364. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157364. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806492 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kockum, I., Huang, J. & Stridh, P. Overview of genotyping technologies and methods. Curr. Protoc.3, e727 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Pacesa, M., Pelea, O. & Jinek, M. Past, present, and future of CRISPR genome editing technologies. Cell187, 1076–1100 (2024). - PubMed
-
- Pardee, K. et al. Rapid, low-cost detection of Zika virus using programmable biomolecular components. Cell165, 1255–1266 (2016). - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

