Response to therapy with direct antiviral drugs in HCV-infected patients with diabetes
- PMID: 40593165
- PMCID: PMC12217250
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-06290-5
Response to therapy with direct antiviral drugs in HCV-infected patients with diabetes
Abstract
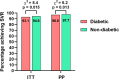
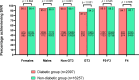
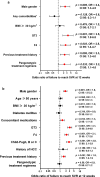
The clinical and metabolic interactions between hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection and diabetes mellitus (DM) are well documented. The study aimed to compare HCV-infected patients with and without DM. The analysis included 18,968 patients treated with direct-acting antivirals (DAAs) between 2015 and 2023, whose data were collected retrospectively. In the study population, 2179 patients (11.5%) were diagnosed with DM. Compared to the non-diabetic population, they were male-dominated (p = 0.003), had a significantly higher proportion of patients aged ≥ 50 years (p < 0.001), and were more burdened with comorbidities (p < 0.001). The most common HCV genotype was 1b with a significantly higher prevalence in the diabetic group (p < 0.001). Liver disease advancement was higher in diabetic patients, with 17.9% advanced fibrosis and 48% cirrhosis compared to 13.2% (p < 0.001) and 21.8% (p < 0.001) in the non-diabetic population. The effectiveness of DAA therapy in patients with DM was significantly lower compared to the population without diabetes, both in intent-to-treat analysis 93.1% vs. 94.6%, p = 0.015, and per-protocol analysis 96.8% vs. 97.7%, p = 0.0128, however, logistic regression analysis did not confirm the role of diabetes as an independent predictor of treatment failure, suggesting that in the absence of other negative prognostic factors, DM alone does not reduce the chances of cure.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Direct-acting antivirals for chronic hepatitis C.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Sep 18;9(9):CD012143. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012143.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28922704 Free PMC article.
-
Direct-acting antivirals for chronic hepatitis C.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jun 6;6(6):CD012143. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012143.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Sep 18;9:CD012143. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012143.pub3. PMID: 28585310 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
NIH Consensus Statement on Management of Hepatitis C: 2002.NIH Consens State Sci Statements. 2002 Jun 10-12;19(3):1-46. NIH Consens State Sci Statements. 2002. PMID: 14768714
-
Pharmacological interventions for acute hepatitis C infection: an attempted network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Mar 13;3(3):CD011644. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011644.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Dec 03;12:CD011644. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011644.pub3. PMID: 28285495 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Extended peginterferon plus ribavirin treatment for 72 weeks versus standard peginterferon plus ribavirin treatment for 48 weeks in chronic hepatitis C genotype 1 infected slow-responder adult patients.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Sep 12;2012(9):CD008516. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008516.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 22972122 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hepatitis, C. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-c.
-
- Westbrook, R. H. & Dusheiko, G. Natural history of hepatitis C. J. Hepatol.61, S58–68 (2014). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

