Developments in MRI radiomics research for vascular cognitive impairment
- PMID: 40593438
- PMCID: PMC12214101
- DOI: 10.1186/s13244-025-02026-1
Developments in MRI radiomics research for vascular cognitive impairment
Abstract
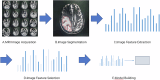
Vascular cognitive impairment (VCI) is an umbrella term for diseases associated with cognitive decline induced by substantive brain damage following pathological changes in the cerebrovascular system. The primary clinical manifestations include behavioral abnormalities and diminished learning and memory cognitive functions. If the location and extent of brain injury are not identified early and therapeutic interventions are not promptly administered, it may lead to irreversible cognitive impairment. Therefore, the early diagnosis of VCI is crucial for its prevention and treatment. Prior to the onset of cognitive impairment in VCI, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) radiomics can be utilized for early assessment and diagnosis, thereby guiding clinicians in providing precise treatment for patients, which holds significant potential for development. This article reviews the classification of VCI, the concept of radiomics, the application of MRI radiomics in VCI, and the limitations of radiomics in the context of advancements in its application within the central nervous system. CRITICAL RELEVANCE STATEMENT: This article explores how MRI radiomics can be used to detect VCI early, enhancing clinical radiology practice by offering a reliable method for prediction, diagnosis, and identification, which also promotes standardization in research and integration of disciplines. KEY POINTS: MRI radiomics can predict VCI early. MRI radiomics can diagnose VCI. MRI radiomics distinguishes VCI from Alzheimer's disease.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Magnetic resonance imaging; Radiomics; Vascular cognitive impairment; White matter lesions.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for Publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




References
Publication types
Grants and funding
- 81960221 to XPY/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82260249 to XPY/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 202311506 to ZYC/Jiangxi Provincial Health Commission Science and Technology Plan project
- 2022A322 to ZYC/Jiangxi Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine science and technology plan project
- 20224BAB216045 to ZYC/Youth Foundation of Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

