Filopodia are essential for steroid release
- PMID: 40593541
- PMCID: PMC12216273
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-60579-7
Filopodia are essential for steroid release
Abstract
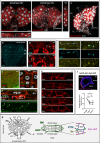
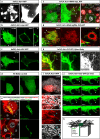
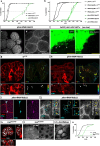
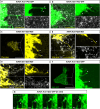
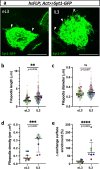
Steroid hormones, crucial for development and physiology, were traditionally believed to diffuse passively through membranes. However, recent evidence shows insect steroid ecdysone being secreted via regulated exocytosis, but the mechanisms ensuring successful hormone release into circulation remain unclear. Our study identifies specialized membrane protrusions, signaling filopodia, in the Drosophila prothoracic gland as essential for vesicle-mediated steroid release. Confocal imaging reveals that these actin- and tubulin-rich structures form a membrane-intertwined basal domain critical for secretion. Disrupting filopodia by interfering with basement membrane interactions-Perlecan or β-integrin-or filopodia-specific protein expression-α-actinin-significantly reduces ecdysone signaling by impairing its release, despite proper production in the gland. Additionally, filopodia dynamics, such as length and density, align with secretion timing and hormone circulating levels, suggesting their role in synchronizing release with physiological needs. The systematic presence of membrane protrusions in steroid-secreting glands across species prompts a comprehensive re-evaluation of steroid release mechanisms.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Sisk, C. L. & Foster, D. L. The neural basis of puberty and adolescence. Nat. Neurosci.7, 1040–1047 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Sapolsky, R. M., Romero, L. M. & Munck, A. U. How do glucocorticoids influence stress responses? Integrating permissive, suppressive, stimulatory, and preparative actions. Endocr. Rev.21, 55–89 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Chu, L. et al. Sex steroid hormones in urinary exosomes as biomarkers for the prediction of prostate cancer. Clin. Chim. Acta531, 389–398 (2022). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

