Tracking international and regional dissemination of the KPC/NDM co-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae
- PMID: 40593598
- PMCID: PMC12216068
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-60765-7
Tracking international and regional dissemination of the KPC/NDM co-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae
Abstract
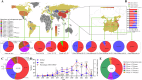
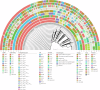
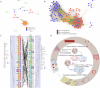
KPC and NDM co-producing carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae (KN-CRKP) showed an upward trend; nevertheless, global systematic and comprehensive analyses profiling remain lacking. 968 local CRKP were collected from 6 provinces in China, and 64,354 genomes were retrieved from GenBank. All 413 genomes of KN-CRKP were obtained from 32 countries, including 16 subtypes of KN-CRKP. The top three CRKP subtypes, K2N1-CRKP, K2N5-CRKP and K3N1-CRKP, exhibited distinct geographic distributions, with K2N1-CRKP and K2N5-CRKP primarily circulating in China while K3N1-CRKP showed predominant prevalence in USA. Meanwhile, ST11-KL64, ST11-KL47, and ST258-KL107, were the three most prevalent ST and KL, and 64.3% of ST11-KL64 KN-CRKP belonged to hypervirulent strains. Genomes revealed Clone Group 1, accounting for 55.0% of KN-CRKP, shifting from KL47 to KL64 and carrying more hypervirulence genes, has a significant advantage in adhesion, invasion, and proliferation, and its dispersal was the primary driver contributing to the worldwide spread of KN-CRKP. Furthermore, ST11 KN-CRKP was generally formed by KPC-producing CRKP acquiring blaNDM-carrying plasmid and novel hybrid plasmids co-encoding KPC and NDM have occurred. Aztreonam/avibactam and cefiderocol were promising antimicrobial agents against KN-CRKP. The global KN-CRKP research, spanning from 2005 to 2024, provides valuable insights into the global transmission, dynamics, and treatment of KN-CRKP.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics approval: This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the China-Japan Friendship Hospital (CJFH, 2022-KY-054).
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

