Analysis of the Rehmannia chingii geneome identifies RcCYP72H7 as an epoxidase in iridoid glycoside biosynthesis
- PMID: 40593652
- PMCID: PMC12214713
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-60909-9
Analysis of the Rehmannia chingii geneome identifies RcCYP72H7 as an epoxidase in iridoid glycoside biosynthesis
Abstract
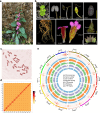
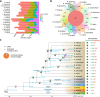
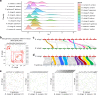
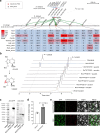
Rehmannia chingii (2n = 2x = 28) is an important folk medicinal plant with high therapeutic value, particularly due to its richness in iridoid glycosides. However, research on its evolution and gene functional identification has been hindered by the lack of a high-quality genome. Here, we present the 1.169 Gb telomere-to-telomere (T2T) genome sequence of R. chingii. Phylogenetic analysis confirms that Rehmannia belongs to the Orobanchaceae family. We find that structural genes of the 2-C-methyl-d-erythritol-4-phosphate (MEP) pathway and the iridoid pathway are predominantly expressed in R. chingii leaves. Further analyses reveal a cytochrome P450 gene cluster localized on chromosome 8, and identify RcCYP72H7 within this cluster as an aucubin epoxidase, capable of catalyzing aucubin epoxidation to form catalpol. The genome offers valuable resources for studying iridoid glycoside biosynthesis and the evolutionary history of Rehmannia, and will help to faciliate genetic improvement of R. chingii for pharmaceutical and health-related applications.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Yang, M. Q. et al. Rehmannia chrysantha (Rehmanniaceae), a new species from Inner Mongolia, northern China. Phytotaxa265, 177 (2016). - DOI
-
- Xia, Z. et al. Identification of DNA barcoding in plants of Rehmannia Libosch. ex Fisch. et Mey. and origin of cultivated Rehmannia glutinosa (in Chinese). Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs47, 648–654 (2016).
-
- Liu, Y. F. et al. Four new iridoid glycosides from the roots of Rehmannia glutinosa. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res.10, 1–9 (2023). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

