Lipoic acid functions in Paneth cells to prevent human intestinal stem cell aging
- PMID: 40593722
- PMCID: PMC12215550
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-61070-z
Lipoic acid functions in Paneth cells to prevent human intestinal stem cell aging
Abstract
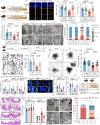
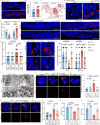
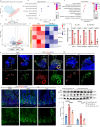
Intestinal stem cell (ISC) aging diminishes the regenerative capacity of the intestinal epithelia, but effective therapeutic strategies to counteract human ISC aging remain elusive. Here, we find that the synthesis of α-lipoic acid (ALA) is reduced in old human small intestine. Notably, ALA supplementation inhibits ISC aging and decreases the number of atypical Paneth cells in old human intestinal organoids and in old mouse small intestines. Importantly, we discern that the effect of ALA on mitigating ISC aging is contingent upon the presence of Paneth cells. Inhibiting the mTOR pathway in Paneth cells with ALA or rapamycin significantly increases cyclic ADP ribose (cADPR) secretion and decreases Notum secretion, which, in turn, enhances ISC functions. In this work, our findings substantiate the role of ALA in inhibiting human ISC aging and present a potential therapeutic approach for managing age-related human intestinal diseases.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Barker, N. Adult intestinal stem cells: critical drivers of epithelial homeostasis and regeneration. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.15, 19–33 (2014). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

