Myosin-dependent short actin filaments contribute to peripheral widening in developing stereocilia
- PMID: 40593742
- PMCID: PMC12215623
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-60976-y
Myosin-dependent short actin filaments contribute to peripheral widening in developing stereocilia
Abstract
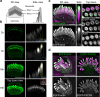
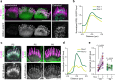
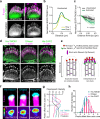
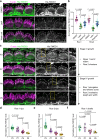
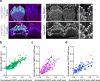
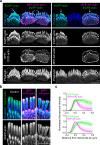
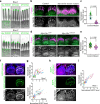
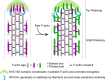
Stereocilia, the actin-based mechanosensory protrusions of inner ear sensory hair cells, require precise dimensional control for proper mechanotransduction, yet the mechanisms governing actin assembly during development remain unclear. Their size and shape are determined by a stable core of long, parallel, unbranched filamentous (F-) actin. We find that during stereocilia widening, which is a key process for function and stability, newly expressed actin first integrates at the tip, then along the periphery of the core. To understand how actin assembles, we probe for globular (G-) actin, F-actin barbed ends, and pointed ends, and identify a tip-enriched population of short actin filaments. Overexpressing actin increases these filaments at the stereocilia periphery, suggesting a role in widening. In addition, the tip-localized myosins MYO3A/B and MYO15A, essential for normal growth, generate or stabilize short filaments. We propose that these short filaments are intermediates that mature into the long F-actin known to comprise the stereocilia core.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Update of
-
Myosin-dependent short actin filaments contribute to peripheral widening in developing stereocilia.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Dec 5:rs.3.rs-5448262. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-5448262/v1. Res Sq. 2024. Update in: Nat Commun. 2025 Jul 1;16(1):5835. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-60976-y. PMID: 39678325 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Schneider, M. E., Belyantseva, I. A., Azevedo, R. B. & Kachar, B. Rapid renewal of auditory hair bundles. Nature418, 837–838 (2002). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01DC015495/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD)
- R01 DC015495/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DC002368/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DC018827/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DC011034/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

