A Hedgehog-Foxf axis coordinates dental follicle-derived alveolar bone formation
- PMID: 40593802
- PMCID: PMC12219665
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-61050-3
A Hedgehog-Foxf axis coordinates dental follicle-derived alveolar bone formation
Abstract
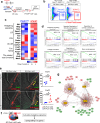
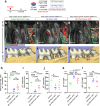
The alveolar bone is a specialized mineralized structure supporting the lifelong functionality of the tooth in mastication. The alveolar bone develops from the dental follicle (DF) during tooth root formation due to deliberate epithelial-mesenchymal interactions. However, how DF progenitor cell fates are regulated toward alveolar bone osteoblasts remains unknown. We find that Hedgehog signaling activities are transiently activated during the onset of tooth root formation and alveolar bone formation. Parathyroid hormone-related protein (PTHrP)-expressing DF cells are highly responsive to Hedgehog signaling, yet constitutive Hedgehog activation using Pthrp-creER and Ptch1-floxed alleles potently suppresses alveolar osteoblast and ligament differentiation of PTHrP+ DF cells, resulting in striking susceptibility to alveolar bone loss. Concomitant inactivation of Hedgehog-target Foxf1 factor in Hedgehog-activated PTHrP+ DF cells partially rescued alveolar bone defects. Therefore, the Hedgehog-Foxf pathway needs to be suppressed to drive alveolar bone osteoblast fates of PTHrP+ DF cells, unraveling a unique tooth-specific mechanism of bone formation requiring deliberate on-off regulations of Hedgehog signaling.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
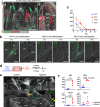
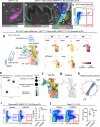

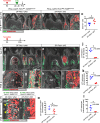

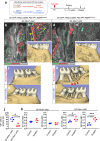

References
-
- Nanci, A. Ten Cate’s Oral Histology-e-Book: Development, Structure, and Function (Elsevier Health Sciences, 2017).
-
- Marx, R. E., Cillo, J. E. & Ulloa, J. J. Oral bisphosphonate-induced osteonecrosis: risk factors, prediction of risk using serum CTX testing, prevention, and treatment. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg.65, 2397–2410 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Pihlstrom, B. L., Michalowicz, B. S. & Johnson, N. W. Periodontal diseases. Lancet366, 1809–1820 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Eke, P. I., Borgnakke, W. S. & Genco, R. J. Recent epidemiologic trends in periodontitis in the USA. Periodontol 200082, 257–267 (2020). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DE029181/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR003167/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01DE030416/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research (NIDCR)
- R01DE029181/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research (NIDCR)
- R01 DE026666/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

