Whole genome sequences of 297 Duolang sheep for litter size
- PMID: 40593870
- PMCID: PMC12215492
- DOI: 10.1038/s41597-025-05448-0
Whole genome sequences of 297 Duolang sheep for litter size
Abstract
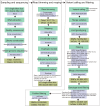
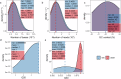
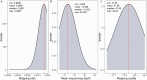
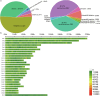
Litter size is a critical economic trait in the sheep industry. Like many other breeds, Duolang sheep typically produce one lamb per ewe per lambing. To date, genetic studies of this trait in that breed have largely relied on candidate gene approaches. To expand the genomic resources for this breed, we sequenced 297 genomes, generating approximately 10.52 trillion bases with an average coverage of 13.35X. High-quality alignments with a mapping rate exceeding 99% enabled the identification of 43,968,128 SNPs and 6,504,047 InDels. This dataset provides a valuable resource for identifying genetic variants associated with litter size through genome-wide association studies (GWAS) and lays the foundation for future genetic improvement efforts through genomic selection in Duolang sheep. Beyond trait mapping, the dataset also supports broader applications, including analyses of genetic diversity, phylogenetic relationships, population history, adaptive introgression, and breed-specific characteristics. Additionally, the moderate-coverage WGS data are suitable for structural variant (SV) detection and downstream analyses such as association mapping and the identification of SVs underlying phenotypic traits.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Whole genome sequencing and structural variations provide insights into the body size traits of Hu sheep.Sci Data. 2025 Aug 6;12(1):1373. doi: 10.1038/s41597-025-05734-x. Sci Data. 2025. PMID: 40770274 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-genome sequencing resources of 301 indigenous Tibetan sheep from the Himalayan region.Sci Data. 2025 Aug 4;12(1):1351. doi: 10.1038/s41597-025-05650-0. Sci Data. 2025. PMID: 40760128 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of new candidate genes affecting drip loss in pigs based on genomics and transcriptomics data.J Anim Sci. 2025 Jan 4;103:skaf177. doi: 10.1093/jas/skaf177. J Anim Sci. 2025. PMID: 40485044 Free PMC article.
-
A meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies to identify candidate genes associated with feed efficiency traits in pigs.J Anim Sci. 2025 Jan 4;103:skaf010. doi: 10.1093/jas/skaf010. J Anim Sci. 2025. PMID: 39847436 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Rapid Identification of the SNP Mutation in the ABCD4 Gene and Its Association with Multi-Vertebrae Phenotypes in Ujimqin Sheep Using TaqMan-MGB Technology.Animals (Basel). 2025 Aug 5;15(15):2284. doi: 10.3390/ani15152284. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40805073 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wolfová, M., Wolf, J., Krupová, Z. & Margetín, M. Estimation of economic values for traits of dairy sheep: II. Model application to a production system with one lambing per year. Journal of dairy science92, 2195–2203 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Wolfová, M., Wolf, J. & Milerski, M. Calculating economic values for growth and functional traits in non‐dairy sheep. Journal of Animal Breeding and Genetetics126, 480–491 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Teletchea, F. in Animal Domestication Ch. Chapter 1 A Brief Overview, 137–159 (Intechopen, 2019).
-
- Souza, C., MacDougall, C., Campbell, B., McNeilly, A. & Baird, D. The Booroola (FecB) phenotype is associated with a mutation in the bone morphogenetic receptor type 1 B (BMPR1B) gene. Journal of Endocrinology169, R1 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Hanrahan, J. P. et al. Mutations in the genes for oocyte-derived growth factors GDF9 and BMP15 are associated with both increased ovulation rate and sterility in Cambridge and Belclare sheep (Ovis aries). Biology of reproduction70, 900–909 (2004). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

