Tanshinone IIA suppresses the proliferation and fibrosis of mesangial cell in diabetic nephropathy though WTAP-mediated m6A methylation
- PMID: 40593882
- PMCID: PMC12216029
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-03738-6
Tanshinone IIA suppresses the proliferation and fibrosis of mesangial cell in diabetic nephropathy though WTAP-mediated m6A methylation
Abstract
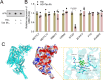
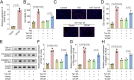
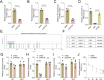
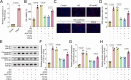
Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is often accompanied by mesangial cell proliferation and fibrosis. Tanshinone IIA (Tan-IIA) is the main fat-soluble component of Salvia miltiorrhiza. N6-Methyladenosine (m6A) modification is a widely studied epigenetic mechanism. This study aimed to investigate the role of Tan-IIA in DN and the underlying mechanism. Cell viability and proliferation were assessed via cell counting kit-8 and ethynyldeoxyuridine assays. Protein levels of fibrosis-related indicators were detected by Western blot. Reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction was used to detect the levels of m6A-related enzymes. The interaction betweenWT1 associated protein (WTAP) and prolactin receptor (PRLR) was examined through RNA immunoprecipitation and dual-luciferase reporter assays. The animal DN models was established. Biochemical measurements of rat serum were performed using commercial kits. Hematoxylin&eosin and Masson trichrome staining were used for histopathological analysis. Results showed that Tan IIA treatment inhibited the cell proliferation and fibrosis of human renal mesangial cells (HRMCs). Besides, Tan IIA treatment regulated WTAP-mediated m6A modification. Overexpression of WTAP upregulated the cell proliferation and fibrosis of HRMCs. Mechanically, WTAP enhanced the stability of PRLR mRNA via m6A methylation. Subsequent rescue investigations revealed that overexpression of PRLR increased the cell proliferation and fibrosis of HRMCs. In the in vivo study, Tan IIA treatment reversed the renal injury in rats and decreased the protein levels of WTAP, PLRP, and fibrosis-related indicators in kidney tissues. Tan IIA suppressed the proliferation and fibrosis of HRMCs in DN though WTAP-mediated m6A methylation of PRLR.
Keywords: Diabetic nephropathy; Fibrosis; PRLR; Proliferation; Tanshinone IIA; WTAP; m6A.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Xiangyang Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine. All animal experiments should comply with the ARRIVE guidelines. All methods were carried out in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

