Enhancing anomaly detection and prevention in Internet of Things (IoT) using deep neural networks and blockchain based cyber security
- PMID: 40593899
- PMCID: PMC12215782
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-04164-4
Enhancing anomaly detection and prevention in Internet of Things (IoT) using deep neural networks and blockchain based cyber security
Abstract
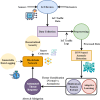
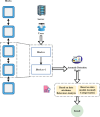
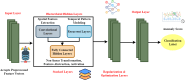
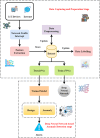
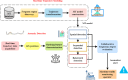
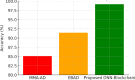
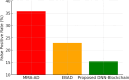
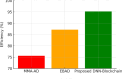
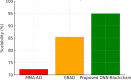
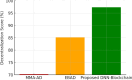
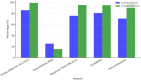
The rapid adoption of Internet of Things (IoT) devices has significantly increased cybersecurity risks, making them vulnerable to anomalies, attacks, and unauthorized access. Traditional security mechanisms struggle to handle the massive data flow, real-time processing requirements, and evolving cyber threats in IoT networks. This paper presents an integrated approach using Deep Neural Networks and Blockchain technology (DNNs-BCT) to enhance anomaly detection and prevention in IoT environments. Our proposed framework employs DNNs for intelligent anomaly detection, leveraging multi-layer feature extraction and adaptive learning mechanisms. The DNN model is trained on IoT traffic datasets to classify network behavior as normal or anomalous, effectively detecting threats such as Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, malware injections, and insider threats. Unlike traditional rule-based intrusion detection systems (IDS), the DNN continuously learns and adapts to new attack patterns, improving detection accuracy and false-positive reduction. This study integrates Blockchain technology into the IoT ecosystem to ensure data integrity, transparency, and decentralized security. Each IoT device logs its activity onto a private blockchain network, preventing data tampering, unauthorized access, and single points of failure. The blockchain employs smart contracts for automated threat response, instantly mitigating malicious activity without human intervention. This distributed ledger approach enhances trust, authentication, and secure communication across IoT devices. The synergy between DNN-based anomaly detection and Blockchain-based security provides a robust, scalable, and adaptive solution for real-time cybersecurity threats in IoT networks. With a low false-positive rate of 15.42% and a strong detection accuracy of 99.18%, the proposed model successfully identifies malicious activity, including malware injections and Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) assaults. Blockchain technology replaces single points of failure and forbids illegal changes by providing data integrity, openness, and decentralizing powers. Furthermore, smart contracts allow autonomous, real-time attack responses, enhancing reaction time efficiency (95.25%) and general system scalability (94.96%).
Keywords: Anomaly detection; Blockchain; Cybersecurity; Deep neural networks; Distributed ledger; Federated learning; Intrusion detection; IoT security; Smart contracts; Threat prevention.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Xu, T. Leveraging blockchain empowered machine learning architectures for advanced financial risk mitigation and anomaly detection. World J. Innov. Mod. Technol.7, 90–100 (2024).
-
- Kumar, P. et al. Digital twin-driven SDN for smart grid: A deep learning integrated blockchain for cybersecurity. Sol. Energy263, 111921 (2023).
-
- Arun, M. et al. Integration of energy storage systems and grid modernization for reliable urban power management toward future energy sustainability. J. Energy Storage114, 115830 (2025).
-
- Sunanda, N., Shailaja, K., Kandukuri, P., Rao, V. S. & Godla, S. R. Enhancing IoT network security: ML and blockchain for intrusion detection. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl.10.14569/IJACSA.2024.0150497 (2024).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

