Leveraging federated learning and edge computing for pandemic-resilient healthcare
- PMID: 40593962
- PMCID: PMC12216392
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-00199-9
Leveraging federated learning and edge computing for pandemic-resilient healthcare
Abstract
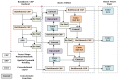
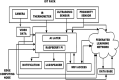
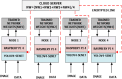
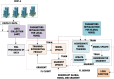
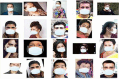
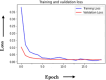
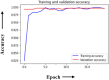
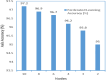
The universal demand for the development and deployment of responsive medical infrastructure and damage control techniques, including the application of technology, is the foremost necessity that emerged immediately in the post-pandemic era. Numerous technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI)-aided decision-making and the Internet of Things (IoT), have been rendered indispensable for such applications. Federated learning (FL) is a popular approach used to enhance AI-driven decision support systems and maintain decentralized learning. As part of a bio-safety norms observance setup, IoT, edge computing, and FL tools can be configured to monitor social distance norms, face-mask use, contact tracing, and cyber-attacks. The design of a pandemic-compliant mechanism for keeping an eye on protocol observance of virus-triggered infectious disease and contact tracing is the subject of this study. The mechanism is based on edge computing, FL frameworks, and a variety of sensors that are connected via IoT. We employ a variety of deep learning pre-trained models (DPTM) as benchmark techniques to compare the performance of the proposed YOLOv4 and SENet attention layer combination. This combination is deployed on a FL framework that is executed using a server and Grove AI-Raspberry Pi 4 blocks act as nodes as part of a human residential premises. The models include the RESNET-50, MobileNetV2, and SocialdistancingNet-19. In particular, the integration of the YoloV4 and SENET attention layer as part of a FL framework delivers dependable performance while addressing facemask detection (94.6%), incorrect facemask detection (98%), facemask classification (95.4%), social distance (96.1%), contact tracing (95.2%) and cyber attack detection (94.2%) while performing tasks like correct and incorrect, proper and improper facemask wearing, monitoring social distancing norms observance, and contact tracing.
Keywords: Contact tracing; Cyber-attack; Deep learning; Deep transfer learning; Edge computing; Facemask; Federated learning; Social distancing.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
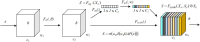





Similar articles
-
Fused federated learning framework for secure and decentralized patient monitoring in healthcare 5.0 using IoMT.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 7;15(1):24263. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-06574-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40624105 Free PMC article.
-
Leveraging multithreading on edge computing for smart healthcare based on intelligent multimodal classification approach.Comput Med Imaging Graph. 2025 Jul 1;124:102594. doi: 10.1016/j.compmedimag.2025.102594. Online ahead of print. Comput Med Imaging Graph. 2025. PMID: 40614479
-
A deep dive into artificial intelligence with enhanced optimization-based security breach detection in internet of health things enabled smart city environment.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 2;15(1):22909. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-05850-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40594312 Free PMC article.
-
Blockchain Integration With Digital Technology and the Future of Health Care Ecosystems: Systematic Review.J Med Internet Res. 2021 Nov 2;23(11):e19846. doi: 10.2196/19846. J Med Internet Res. 2021. PMID: 34726603 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of artificial intelligence on the endoscopic assessment of inflammatory bowel disease-related neoplasia.Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2025 Jun 23;18:17562848251348574. doi: 10.1177/17562848251348574. eCollection 2025. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40556746 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lefringhausen, C. T. Covid-19 vaccines-an australian review. J. Clin. Exp. Immunol.7(3), 491–508 (2022).
-
- WHO. Bulletin of who at https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/covid-19-epidemiological-update-... (WHO, 2020).
-
- Article. Reports of european centre for disease prevention and control at. https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/covid-19/variants-concern (2024).
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

