Enhanced security for medical images using a new 5D hyper chaotic map and deep learning based segmentation
- PMID: 40593969
- PMCID: PMC12215922
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-04906-4
Enhanced security for medical images using a new 5D hyper chaotic map and deep learning based segmentation
Abstract
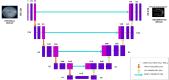
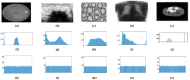
Medical image encryption is important for maintaining the confidentiality of sensitive medical data and protecting patient privacy. Contemporary healthcare systems store significant patient data in text and graphic form. This research proposes a New 5D hyperchaotic system combined with a customised U-Net architecture. Chaotic maps have become an increasingly popular method for encryption because of their remarkable characteristics, including statistical randomness and sensitivity to initial conditions. The significant region is segmented from the medical images using the U-Net network, and its statistics are utilised as initial conditions to generate the new random sequence. Initially, zig-zag scrambling confuses the pixel position of a medical image and applies further permutation with a new 5D hyperchaotic sequence. Two stages of diffusion are used, such as dynamic DNA flip and dynamic DNA XOR, to enhance the encryption algorithm's security against various attacks. The randomness of the New 5D hyperchaotic system is verified using the NIST SP800-22 statistical test, calculating the Lyapunov exponent and plotting the attractor diagram of the chaotic sequence. The algorithm validates with statistical measures such as PSNR, MSE, NPCR, UACI, entropy, and Chi-square values. Evaluation is performed for test images yields average horizontal, vertical, and diagonal correlation coefficients of -0.0018, -0.0002, and 0.0007, respectively, Shannon entropy of 7.9971, Kolmogorov Entropy value of 2.9469, NPCR of 99.61%, UACI of 33.49%, Chi-square "PASS" at both the 5% (293.2478) and 1% (310.4574) significance levels, key space is 2500 and an average encryption time of approximately 2.93 s per 256 × 256 image on a standard desktop CPU. The performance comparisons use various encryption methods and demonstrate that the proposed method ensures secure reliability against various challenges.
Keywords: Critical region segmentation; Dynamic DNA encoding; Hyper-chaotic map; Image encryption; U-Net; Zig-zag scrambling.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics approval: All authors have read, understood, and have complied as applicable with the statement on “Ethical responsibilities of Authors” as found in the Instructions for Authors.
Figures




















Similar articles
-
A new medical image encryption using modular integrated logistic exponential map and multi-level Q-Sequence matrix.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 26;15(1):31383. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-16343-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40858669 Free PMC article.
-
Robust Image Encryption with 2D Hyperchaotic Map and Dynamic DNA-Zigzag Encoding.Entropy (Basel). 2025 Jun 6;27(6):606. doi: 10.3390/e27060606. Entropy (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40566193 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing AES image encryption with a three-dimensional hyperchaotic system for increased security and efficiency.PLoS One. 2025 Jul 18;20(7):e0328297. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0328297. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40680055 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
Cited by
-
A lightweight multi round confusion-diffusion cryptosystem for securing images using a modified 5D chaotic system.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 30;15(1):31986. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-13290-y. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40885745 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rohhila, S. & Singh, A. K. Deep learning-based encryption for secure transmission digital images: A survey. Comput. Electr. Eng.116, 109236 (2024).
-
- Zia, U. et al. Survey on image encryption techniques using chaotic maps in spatial, transform and spatiotemporal domains. Int. J. Inf. Secur.21, 917–935 (2022).
-
- Singh, A. K., Anand, A., Lv, Z., Ko, H. & Mohan, A. A survey on healthcare data: A security perspective. ACM Trans. Multimed. Comput. Commun. Appl.17, 1–26 (2021).
-
- Prasad, S. & Singh, A. K. Survey on medical image encryption: From classical to deep learning-based approaches. Comput. Electr. Eng.123, 110011 (2025).
-
- Khurana, N. & Dua, M. A novel one-dimensional Cosine within Sine chaotic map and novel permutation–diffusion based medical image encryption. Nonlinear Dyn.109, 1–21 (2024).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

