Novel machine learning approach for enhanced smart grid power use and price prediction using advanced shark Smell-Tuned flexible support vector machine
- PMID: 40594020
- PMCID: PMC12217175
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-05083-0
Novel machine learning approach for enhanced smart grid power use and price prediction using advanced shark Smell-Tuned flexible support vector machine
Abstract
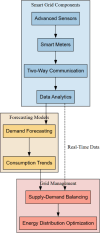
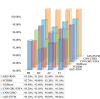
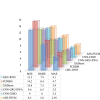
Energy management has enhanced sustainability, dependability, and efficiency in smart grids. Urbanisation, technology, and consumer behaviour have boosted need for innovative power use and price control systems. The paper intends to construct ML for smart grid power use and price prediction. This work used an advanced shark smell-tuned flexible support vector machine (ASS-FSVM) to forecast smart grid price and power use. Weather stations, smart meters, and market price databases document power use and pricing. The quality and consistency of data are enhanced via the processes of cleaning and normalizing inputs. PCA reduces dimensionality by extracting pre-processed data characteristics. Optimized and tested FSVM models can anticipate smart grid power use and pricing. ASS may identify the most important dataset properties. The research evaluates electricity consumption forecasting using accuracy (98.05%), recall (98.93%), precision (97.10%), and F1-score (98.04%), and electricity price predicting using MAPE (4.32%), RMSE (5.80%), MSE (8.50%), and MAE (2.95%). The recommended strategy greatly increases forecast accuracy, helping utilities improve grid stability, demand responsiveness, and customer pricing.
Keywords: Advanced shark smell tuned flexible support vector machines (ASS-FSVM); Electricity consumption; Pricing; Principal component analysis (PCA); Smart grids.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Effectiveness of Wearable Devices Using Artificial Intelligence for Blood Glucose Level Forecasting or Prediction: Systematic Review.J Med Internet Res. 2023 Mar 14;25:e40259. doi: 10.2196/40259. J Med Internet Res. 2023. PMID: 36917147 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
-
REDf: a deep learning model for short-term load forecasting to facilitate renewable integration and attaining the SDGs 7, 9, and 13.PeerJ Comput Sci. 2025 Apr 23;11:e2819. doi: 10.7717/peerj-cs.2819. eCollection 2025. PeerJ Comput Sci. 2025. PMID: 40567641 Free PMC article.
-
Design of an improved graph-based model integrating LSTM, LoRaWAN, and blockchain for smart agriculture.PeerJ Comput Sci. 2025 Jun 20;11:e2896. doi: 10.7717/peerj-cs.2896. eCollection 2025. PeerJ Comput Sci. 2025. PMID: 40567697 Free PMC article.
-
Supervised Machine Learning Models for Predicting Sepsis-Associated Liver Injury in Patients With Sepsis: Development and Validation Study Based on a Multicenter Cohort Study.J Med Internet Res. 2025 May 26;27:e66733. doi: 10.2196/66733. J Med Internet Res. 2025. PMID: 40418571 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Avancini, D. B. et al. A new IoT-based smart energy meter for smart grids. Int. J. Energy Res.45 (1), 189–202 (2021).
-
- Kim, M. K., Kim, Y. S. & Srebric, J. Predictions of electricity consumption in a campus building using occupant rates and weather elements with sensitivity analysis: Artificial neural network vs. linear regression. Sustainable Cities and Society, 62, p.102385. (2020).
-
- Mbey, C. F., FobaKakeu, V. J., Boum, A. T. & YemSouhe, F. G. Solar photovoltaic generation and electrical demand forecasting using multi-objective deep learning model for smart grid systems. Cogent Engineering, 11(1), p.2340302. (2024).
-
- Souhe, F. G. Y., Mbey, C. F., Boum, A. T. & Ele, P. Forecasting of electrical energy consumption of households in a smart grid. Int. J. Energy Econ. Policy. 11 (6), 221–233 (2021).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

