Enhancing intercultural competence in technical higher education through AI-driven frameworks
- PMID: 40594064
- PMCID: PMC12217878
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-03303-1
Enhancing intercultural competence in technical higher education through AI-driven frameworks
Abstract
The assessment of Intercultural Competence (IC) is increasingly recognized as an essential component of students' professional competency development in higher education settings. This study looks at the objectives of creating ICC and offers an assessment framework that adheres to the competency cultivation principles and the IC acquisition model. However, because intercultural communicative competence is not given enough attention, there are still problems with teaching abroad. This study utilizes the AI approaches for assessing the ICC in higher education. The Apriori algorithm analyses the association among the instructional tasks and ICC learning outcomes to find the teaching strategies most effectively build the cultural knowledge. Fuzzy logic is utilized to convert the qualitative perceptions to quantifiable data to address the subjective assessment, Sim Rank evaluate the student performance similarity and behavior to find the clusters and MK means used to segment the students based on ICC profiles for targeted interventions. The concepts and methods of model construction were applied in the development of a fuzzy thorough assessment model for college students' ICC. The findings show a substantial relationship between the total IC level and the four IC components of attitude, knowledge, Skill and consciousness. According to correlation strength, these characteristics are rated as follows: attitude (0.835), skill A (0.885), Skill B (0.823), Consciousness (0.714) and knowledge (0.972). Furthermore, there is a positive association between cross-cultural factors and the five aspects of English language ability, indicating a reciprocal relationship between developing IC and learning English.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Clustering; Fuzzy; Higher education; Interculture competence.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

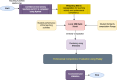
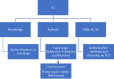



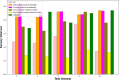

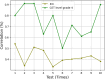
References
-
- Rahiman, H. U. & &Kodikal, R. Revolutionizing education: artificial intelligence empowered learning in higher education. Cogent Educ.11, 2293431. 10.1080/2331186X.2023.2293431 (2023). - DOI
-
- Byram, M. Teaching and Assessing Intercultural Communicative Competence: Revisited (Multilingual Matters, 2021). 10.21832/9781800410251
-
- Khasawneh, M. A. S. The potential of AI in facilitating Cross-Cultural communication through translation. J. Namibian Stud.10.59670/jns.v37i.4654 (2023). - DOI
-
- Sintawati, W., Kerimbayev, N., &Altinay, F. & Systematic Review : Exploring Technology Supported Cross-Cultural Learning through Review Studies. Sustainability2024 16, 755. (2003). –2023 10.3390/su16020755
-
- Akdere, M., Acheson, K. & Jiang, Y. An examination of the effectiveness of virtual reality technology for intercultural competence development. Int. J. Intercultural Relat.82, 109–120. 10.1016/j.ijintrel.2021.03.009 (2021). - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

