A deep dive into artificial intelligence with enhanced optimization-based security breach detection in internet of health things enabled smart city environment
- PMID: 40594312
- PMCID: PMC12216786
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-05850-z
A deep dive into artificial intelligence with enhanced optimization-based security breach detection in internet of health things enabled smart city environment
Abstract
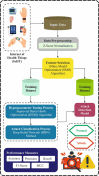
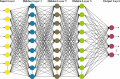
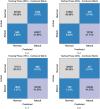
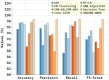
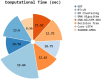
Internet of Health Things (IoHT) plays a vital role in everyday routine by giving electronic healthcare services and the ability to improve patient care quality. IoHT applications and devices become widely susceptible to cyber-attacks as the tools are smaller and varied. Additionally, it is of dual significance once IoHT contains tools applied in the healthcare field. In the context of smart cities, IoHT enables proactive health management, remote diagnostics, and continuous patient monitoring. Therefore, it is essential to advance a strong cyber-attack detection method in the IoHT environments to mitigate security risks and prevent devices from being vulnerable to cyber-attacks. So, improving an intrusion detection system (IDS) for attack identification and detection using the IoHT method is fundamentally necessary. Deep learning (DL) has recently been applied in attack detection because it can remove and learn deeper features of known attacks and identify unknown attacks by analyzing network traffic for anomalous patterns. This study presents a Securing Attack Detection through Deep Belief Networks and an Advanced Metaheuristic Optimization Algorithm (SADDBN-AMOA) model in smart city-based IoHT networks. The main aim of the SADDBN-AMOA technique is to provide a resilient attack detection method in the IoHT environment of smart cities to mitigate security threats. The data pre-processing phase applies the Z-score normalization method for converting input data into a structured pattern. For the selection of the feature process, the proposed SADDBN-AMOA model designs a slime mould optimization (SMO) model to select the most related features from the data. Followed by the deep belief network (DBN) method is used for the attack classification method. Finally, the improved Harris Hawk optimization (IHHO) approach fine-tunes the hyperparameter values of the DBN method, leading to superior classification performances. The effectiveness of the SADDBN-AMOA method is investigated under the IoT healthcare security dataset. The experimental validation of the SADDBN-AMOA method illustrated a superior accuracy value of 98.71% over existing models.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Attack detection; Feature selection; Harris Hawk optimization; Internet of health things; Intrusion detection systems; Smart cities.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics approval: This article contains no studies with human participants performed by any authors.
Figures
References
-
- Aruna Santhi, J. & Vijaya Saradhi, T. Attack detection in medical internet of things using optimized deep learning: Enhanced security in healthcare sector. Data Technol. Appl.55 (5), 682–714 (2021).
-
- Saheed, Y. K. & Arowolo, M. O. Efficient cyber-attack detection on the internet of medical things-smart environment based on deep recurrent neural network and machine learning algorithms. IEEe Access.9, 161546–161554 (2021).
-
- Shankar, K. Improving the security and authentication of the cloud with IoT using hybrid optimization based quantum hash function. J. Intell. Syst. Internet Things. 1 (2), 61–61 (2021).
-
- Ravi, V., Pham, T. D. & Alazab, M. Deep learning-based network intrusion detection system for internet of medical things. IEEE Internet Things Mag. 6 (2), 50–54 (2023).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

