Deep learning based classification of tibio-femoral knee osteoarthritis from lateral view knee joint X-ray images
- PMID: 40594325
- PMCID: PMC12219435
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-04869-6
Deep learning based classification of tibio-femoral knee osteoarthritis from lateral view knee joint X-ray images
Erratum in
-
Correction: Deep learning based classification of tibio-femoral knee osteoarthritis from lateral view knee joint X-ray images.Sci Rep. 2025 Sep 3;15(1):32363. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-17772-x. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40903478 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
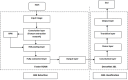
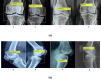
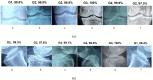
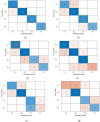
Design an effective deep learning-driven method to locate and classify the tibio-femoral knee joint space width (JSW) with respect to both anterior-posterior (AP) and lateral views. Compare the results and see how successfully a deep learning approach can locate and classify tibio-femoral knee joint osteoarthritis from both anterior-posterior (AP) and lateral-view knee joint x-ray images. To evaluate the performance of a deep learning approach to classify and compare radiographic tibio-femoral knee joint osteoarthritis from both AP and lateral view knee joint digital X-ray images. We use 4334 data points (knee X-ray images) for this study. This paper introduces a methodology to locate, classify, and compare the outcomes of tibio-femoral knee joint osteoarthritis from both AP and lateral knee joint x-ray images. We have fine-tuned DenseNet 201 with transfer learning to extract the features to detect and classify tibio-femoral knee joint osteoarthritis from both AP view and lateral view knee joint X-ray images. The proposed model is compared with some classifiers. The proposed model locate the tibio femoral knee JSW localization accuracy at 98.12% (lateral view) and 99.32% (AP view). The classification accuracy with respect to the lateral view is 92.42% and the AP view is 98.57%, which indicates the performance of automatic detection and classification of tibio-femoral knee joint osteoarthritis with respect to both views (AP and lateral views).We represent the first automated deep learning approach to classify tibio-femoral osteoarthritis on both the AP view and the lateral view, respectively. The proposed deep learning approach trained on the femur and tibial bone regions from both AP view and lateral view digital X-ray images. The proposed model performs better at locating and classifying tibio femoral knee joint osteoarthritis than the existing approaches. The proposed approach will be helpful for the clinicians/medical experts to analyze the progression of tibio-femoral knee OA in different views. The proposed approach performs better in AP view than Lateral view. So, when compared to other continuing existing architectures/models, the proposed model offers exceptional outcomes with fine-tuning.
Keywords: AP view; DenseNet 201; Digital X-ray images; Lateral view; Tibio-femoral osteoarthritis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Consent to participate: A waiver for informed consent of the patients was provided by the Code of Ethics committee (CEC) constituted by the Kalasalingam Academy of Research and Education due to the retrospective and observational nature of our study. Ethical approval: The experimental protocol for the study was approved by the Code of Ethics Committee (CEC) of Kalasalingam Academy of Research and Education (Reference: KARE/CEC/MoM/2024–2025/01 dated 20.07.2024). All procedures performed in this studies involving human participants adhered to the ethical standards of the institution and were conducted in compliance with the principles outlined in the 1964 Helsinki Declaration. This ensures that the research upholds the highest ethical standards, safeguarding the rights, dignity, and well-being of all participants involved. Informed consent: The Code of Ethics Committee (CEC) of Kalasalingam Academy of Research and Education has made the decision to waive the need for informed consent for a proposed research study involving the use of a dataset of knee X-ray images (Reference: KARE/CEC/MoM/2024–2025/01 dated 20.07.2024). This decision is based on the fact that the study uses anonymized images of subjects, not directly involving interactions with or identifying details of patients. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Conaghan, P. G. et al. Impact and therapy of osteoarthritis: the arthritis care OA Nation 2012 survey. Clin. Rheumatol.10.1007/s10067-014-2692-1 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Demehri, S., Hafezi-Nejad, N. & Carrino, J. A. Conventional and novel imaging modalities in osteoarthritis: current state of the evidence. J. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol.10.1097/BOR.0000000000000163 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Cibere, J. Do we need radiographs to diagnose osteoarthritis? Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol.10.1016/j.berh.2005.08.001 (2006). - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

