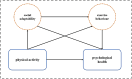
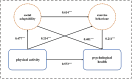
Physical activity enhances college students' mental health through social adaptability and exercise behavior chain mediation
- PMID: 40594661
- PMCID: PMC12214962
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-07791-z
Physical activity enhances college students' mental health through social adaptability and exercise behavior chain mediation
Abstract
With increasing levels of stress among university students, it is essential to explore how institutional resources can support mental well-being. This study examines the impact of physical education (PE) classes on students’ mental health and investigates the mediating roles of physical activity and social adaptability. A survey was conducted among 525 university students. The study introduced two key variables—social adaptability and physical activity—and employed a structural model to assess the direct and indirect effects of PE on mental health. Findings indicate that participation in PE classes contributes positively to students’ mental well-being. Moreover, PE enhances mental health indirectly by promoting greater social adaptability and increased physical activity. A significant correlation was found between social adaptability and physical activity, illustrating a clear pathway linking these factors. Notably, a considerable proportion of students reported insufficient physical activity, highlighting the need for PE programs to further encourage active lifestyles. University PE classes play a valuable role in supporting students’ mental health, not only through direct psychological benefits but also by fostering social integration and encouraging physical activity. These findings underscore the dual importance of PE for both mental and physical well-being.
Keywords: Chain mediation model; Exercise behavior; Physical education; Psychological health; Social adaptability.
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics statement: We confirm that all methods were performed in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations. We confirm that all experimental protocols were approved by the Life Sciences Ethics Review Committee of Zhengzhou University (FWA00014064). We confirm that informed consent was obtained from all subjects.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of physical exercise on college students' sense of meaning in life: the chain mediating role of stress perception and mental toughness.Front Psychol. 2025 Jun 4;16:1612957. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1612957. eCollection 2025. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40535180 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship between college students' psychological resilience and autonomous fitness behavior: a moderated mediation model.Front Psychol. 2025 Jun 4;16:1513031. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1513031. eCollection 2025. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40535185 Free PMC article.
-
Analysing the effect of physical exercise on social anxiety in college students using a chained mediation model.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 20;15(1):2475. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-87140-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39833375 Free PMC article.
-
The Dynamic Impact of Physical Education Teacher Support on College Students' Adherence to Exercise: A Cross-Lagged Study from the Perspective of Self-Determination Theory.Behav Sci (Basel). 2025 Jun 11;15(6):802. doi: 10.3390/bs15060802. Behav Sci (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40564584 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between physical exercise and college students' social adaptation: the chain mediating role of self-esteem and peer attachment.Front Psychol. 2024 Oct 29;15:1453675. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1453675. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 39534472 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burris, J. L., Brechting, E. H., Salsman, J. & Carlson, C. R. Factors associated with the psychological Well-Being and distress of university students. J. Am. Coll. Health. 57, 536–543 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Creo, E. D., Mareque, M. & Portela-Pino, I. The acquisition of teamwork skills in university students through extra-curricular activities. Educ. Train.63, 165–181 (2021).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources