An intricate role of Ang II/AT1 in the modulation of monosodium glutamate-induced pulmonary fibrosis by TGF-β/Smad through quercetin
- PMID: 40594711
- PMCID: PMC12214936
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-05781-9
An intricate role of Ang II/AT1 in the modulation of monosodium glutamate-induced pulmonary fibrosis by TGF-β/Smad through quercetin
Abstract
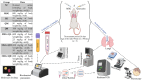
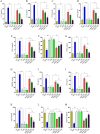
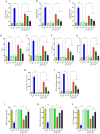
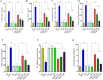
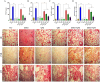
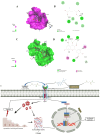
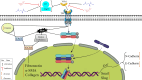
To investigate the protective actions of the natural flavonoid quercetin against monosodium glutamate (MSG)-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats, the present study targets the modulation of the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway and the involvement of Ang II/AT1. The experimental model involved the treatment of rats with MSG (0.6 g/kg body weight) for 4 weeks and quercetin dosages of 25 mg, 50 mg, and 100 mg/kg body weight. The study applied the combination of biochemical, molecular, and histopathological evaluation to identify the role of quercetin in impacting major cytokines (IL-17, IL-19, TGF-β, VEGF), oxidative stress markers (TBARS, NO, SOD, CAT, GSH), extracellular matrix components (collagen-I, α-SMA, fibronectin), and fibrosis gene expression (TGF-β1, Smad2/3/4, CTGF, Snail, Slug). MSG treatment increased pro-fibrotic cytokines, oxidative stress, and deposition of collagen in a significant amount, while administration of quercetin dose-dependently reversed the alterations. Quercetin also reversed the activity of antioxidant enzymes, reduced inflammatory cytokines, and inhibited TGF-β/Smad signaling as indicated by lowered TGF-β receptor II activation and following Smad phosphorylation. Molecular docking demonstrated that quercetin competitively binds to TGF-β receptor II to inhibit MSG-induced fibrotic signaling. Quercetin inhibits MSG-induced lung fibrosis by inhibiting collagen accumulation and inflammatory cell invasion and has the potential to produce therapeutic effects by modulating TGF-β/Smad signaling and restoring lung tissue homeostasis.
Keywords: Monosodium glutamate; Oxidative stress; Pro-fibrotic cytokines; Pulmonary fibrosis; Quercetin; TGF-β/Smad.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The therapeutic role of Coccinia grandis in flavor-enhancing high-lipid diet-induced chronic kidney disease: a dual role of NF-kB and TGF-β/smad in renal fibrosis.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Aug 7;52(1):798. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10798-4. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40775474
-
Codonopsis radix improves bleomycin-induced idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis by regulating TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway and inhibiting fibroblast differentiation and proliferation.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Aug 29;352:120233. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2025.120233. Epub 2025 Jul 5. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40619039
-
Ugonin L ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis as a novel TβRs inhibitor by regulating the TGF-β/TβRs signaling and autophagy.Biomed Pharmacother. 2025 Aug;189:118267. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2025.118267. Epub 2025 Jun 18. Biomed Pharmacother. 2025. PMID: 40532575
-
Effective dose/duration of natural flavonoid quercetin for treatment of diabetic nephropathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis of rodent data.Phytomedicine. 2022 Oct;105:154348. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154348. Epub 2022 Jul 19. Phytomedicine. 2022. PMID: 35908521
-
The construction of preclinical evidence for the treatment of liver fibrosis with quercetin: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Phytother Res. 2022 Oct;36(10):3774-3791. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7569. Epub 2022 Aug 2. Phytother Res. 2022. PMID: 35918855
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

