Enhancing urban quality of life evaluation using spatial multi criteria analysis
- PMID: 40594757
- PMCID: PMC12218988
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-05468-1
Enhancing urban quality of life evaluation using spatial multi criteria analysis
Abstract
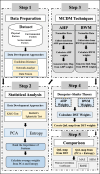
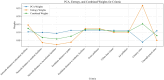
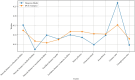
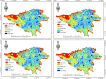
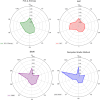
Quality of Life (QoL) in urban environments represents people's well-being and is influenced by various factors. This paper introduces an innovative approach to promote urban equity by integrating spatial analysis and Multi-Criteria Decision-Making (MCDM). The proposed method focuses mainly on accessibility to urban facilities and environmental health factors. In this research, data fusion techniques were utilized to generate criteria maps for urban air pollution and heat islands, while factor analysis, Principal Component Analysis (PCA), and entropy were employed to provide a comprehensive assessment of equity related to these environmental factors in the case study area. Expert opinions, collected through the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) and Best-Worst Method (BWM), were refined using Dempster-Shafer theory to adjust the weights assigned to each evaluation criterion. The results highlight that access to educational facilities and green spaces significantly impacts urban equity, with respective weights of 0.189 and 0.149. Air pollution was also identified as a critical factor, with a weight of 0.152. These findings underscore the potential of this integrated approach in assessing urban livability, particularly in Tehran, Iran.
Keywords: Analytic hierarchy process; Best–Worst method; Dempster–Shafer theory; Principal component analysis; Urban quality of life.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interest: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Leitmann, J., Bartone, C. & Bernstein, J. Environmental management and urban development issues and options for Third World cities. Environ. Urban.4(2), 131–140. 10.1177/095624789200400213 (1992). - DOI
-
- Huang, J. Strategic thinking on the new urbanization road in the era of ecological civilization. Eco Cities1(1), 1–12. 10.54517/ec.v1i1.1824 (2020). - DOI
-
- Lo, C. P. & Faber, B. J. Integration of landsat thematic mapper and census data for quality of life assessment. Remote Sens. Environ.62(2), 143–157. 10.1016/S0034-4257(97)00088-6 (1997). - DOI
-
- Rinner, C. A geographic visualization approach to multi-criteria evaluation of urban quality of life. Int. J. Geographical Inform. Sci.21(8), 907–919. 10.1080/13658810701349060 (2007). - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

