Impact of low-intensity 463 nm blue light on proliferation and adaptive mutation of Escherichia coli DH5α cells
- PMID: 40594907
- PMCID: PMC12215020
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-06596-4
Impact of low-intensity 463 nm blue light on proliferation and adaptive mutation of Escherichia coli DH5α cells
Abstract
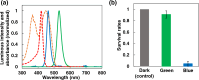
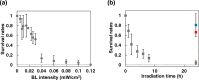
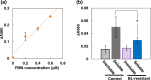
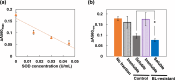
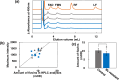
The growth rate of many microorganisms decreases when exposed to blue light (BL) at around 450 nm. This growth retardation is likely caused by the photosensitivity of endogenous photosensitizers, flavins, which absorb BL and generate reactive oxygen species (ROS) that cause inactivation and mutations of microorganisms. In this study, the effect of weak (0-0.12 mW/cm2) 463 nm BL on E. coli (DH5α) cell proliferation was investigated. Surprisingly, BL of only 0.03 mW/cm2 reduced the DH5α colony number by 52%, and about 5% of cells (BL-resistant cells) formed colonies under 0.1 mW/cm2 BL. Five-generation subculturing suggested that the BL-resistant cells underwent mutation(s) and adapted to grow under a BL environment. Fewer superoxide anion radicals were generated by BL irradiation in BL-resistant cells than in control DH5α cells because of the lower amount of intracellular flavins in BL-resistant cells. Our data suggest that the main photosensitizer of 463 nm BL is flavins, and ROS generated by BL-activated flavins induces inactivation and mutation(s) of DH5α cells. BL-resistant mutant cells with low amounts of intracellular flavins may reproducibly be generated by mutation(s) and preferentially proliferate under BL conditions.
Keywords: E. coli (DH5α); Blue light; Flavins; Reactive oxygen species (ROS); Stress-induced adaptive mutation.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Supplementary Information: Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to O.H.
Figures

References
-
- Pham, T. T. et al. Inactivating Escherichia coli using hexagonal array of narrow bandwidth of violet-blue light emitting diode. Case Studies in Chemical and Environmental Engineering (CSCEE).8, 100389. 10.1016/j.cscee.2023.100389 (2023). - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

