The predictive value of triglyceride glucose-body mass index for contrast-induced nephropathy in patients with acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention
- PMID: 40595003
- PMCID: PMC12216597
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-07212-1
The predictive value of triglyceride glucose-body mass index for contrast-induced nephropathy in patients with acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention
Abstract
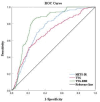
Triglyceride glucose-body mass index (TyG-BMI) is an indicator of insulin resistance (IR) and is associated with an increased risk of adverse cardiovascular events. Insulin resistance (IR) is an important pathogenesis of diabetes mellitus, and also an important factor affecting the incidence and prognosis of cardiovascular diseases. However, the relationship between TyG-BMI and CIN in patients with STEMI has not been studied. STEMI patients who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) between January 2017 and July 2020 were selected consecutively. The occurrence of contrast-induced nephropathy (CIN) is determined by the serum creatinine concentration. A total of 1041 patients (813; 78.1% male) with STEMI who underwent primary PCI were enrolled in this retrospective study. The registered cohort was divided into 2 groups according to whether the subjects developed CIN after surgery. CIN was defined as an increase in serum creatinine > 25% or 0.5 mg/dL from baseline in the first 48 to 72 h after PCI. A total of 201 cases (19.3%) of CIN were diagnosed. Compared with CIN (-) patients, CIN (+) patients had larger BMI, higher proportion of hypertension and hyperlipidemia, higher levels of fasting blood glucose, total cholesterol, triglyceride and uric acid, and higher levels of metabolic score for insulin resistance (METS-IR), triglyceride-glucose index (TyG) and TyG-BMI. Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that TyG-BMI (OR = 1.029,95%CI 1.011-1.047, P = 0.002) were the independent risk factors for CIN in STEMI patients after primary PCI. ROC curve analysis showed that TyG-BMI had a high predictive value for CIN (AUC = 0.812; 95%CI 0.784-0.840), the best cut-off value was 196.34, the sensitivity was 85.6%, and the specificity was 73.1%. TyG-BMI is an independent risk factor for CIN after pPCI in STEMI patients and has a good predictive effect for the occurrence of CIN after pPCI.
Keywords: Contrast-induced nephropathy; Metabolic score for insulin resistance; ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction; Triglyceride glucose-BMI; Triglyceride-glucose index.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Role of Magnesium Levels in the Progression of Contrast-Induced Nephropathy in Patients With STEMI Undergoing Primary PCI.Angiology. 2025 Jul;76(6):572-579. doi: 10.1177/00033197251314629. Epub 2025 Jan 22. Angiology. 2025. PMID: 39838962
-
Association of triglyceride-glucose index and estimated glucose disposal rate with outcomes in patients with acute myocardial infarction: Cumulative effect and mediation analysis.PLoS One. 2025 Jul 23;20(7):e0328150. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0328150. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40700433 Free PMC article.
-
Association between insulin resistance indices and outcomes in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 Jan 22;24(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02595-x. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 39844150 Free PMC article.
-
Triglyceride-glucose-body mass index and the incidence of cardiovascular diseases: a meta-analysis of cohort studies.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 Jan 22;24(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02584-0. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 39844258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development and validation of an AMR-based predictive model for post-PCI contrast-induced nephropathy in patients with acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025 Jun 26;12:1552762. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1552762. eCollection 2025. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025. PMID: 40642748 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- M Süleymanoğlu İ Rencüzoğulları Y Karabağ 2020 The relationship between atherogenic index of plasma and no-reflow in patients with acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction who underwent primary percutaneous coronary intervention Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging. 36 5 789 796 - PubMed
-
- M Karakayali M Ogun I Artac 2025 Serum malondialdehyde levels at admission as a predictor of inhospital mortality in patients with acute coronary syndrome Coron Artery Dis. 36 3 211 217 - PubMed
-
- M Karakayali T Omar I Artac 2023 The prognostic value of HALP score in predicting in-hospital mortality in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention Coron Artery Dis. 34 7 483 488 - PubMed
-
- D Giacoppo G Gargiulo S Buccheri 2017 Preventive strategies for contrast-induced acute kidney injury in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary procedures: evidence from a hierarchical Bayesian network meta-analysis of 124 trials and 28 240 patients Circ. Cardiovasc. Interv. 10 5 e004383 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous