Synthesis, biological evaluation, pharmacological profiling, and molecular docking studies of 4-Aminocoumarin based phenyliodonium derivatives as potent therapeutic agents
- PMID: 40595397
- PMCID: PMC12218390
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-95078-8
Synthesis, biological evaluation, pharmacological profiling, and molecular docking studies of 4-Aminocoumarin based phenyliodonium derivatives as potent therapeutic agents
Abstract
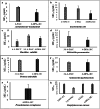
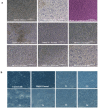
4-Aminocoumarins are significant in organic synthesis as key building blocks for various heterocyclic structures with pharmacological importance. This study focuses on synthesizing phenyliodonium derivatives of 4-aminocoumarins (T1-T6) and evaluating their broad-spectrum biological properties, including antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral, antioxidant, cytotoxicity, and wound-healing properties. The compounds synthesized were structurally confirmed through UV-Vis, GC-MS, 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR, FT-IR, melting point, and CHNS analysis. The in vitro antibacterial and antifungal activities of these compounds were assessed against eight bacterial strains and five plant fungal pathogens. The antiviral property was evaluated by measuring the reduction in cytopathic effects of Dengue virus type-2 in BHK-21 cells. Cytotoxicity testing on human epidermal keratinocyte cells using the MTT assay at concentrations ranging from 1 to 100 µg/mL revealed that none of the compounds exhibited significant cytotoxic effects. Additionally, ADME/Toxicity, molecular docking, antioxidant, and wound-healing studies were examined, further supporting the therapeutic potential of these compounds. Most of the synthesized phenyliodonium derivatives demonstrated broad-spectrum antibacterial and antifungal activities. Among them, Compound T6 exhibited the most potent antimicrobial activity, as indicated by its MIC₉₀ and MBC values, demonstrating superior efficacy compared to ciprofloxacin. The antiviral test against Dengue virus type-2 showed minimal effects with a cytopathic effect reduction of 10-13% at non-toxic concentrations. These compounds exhibited broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity coupled with minimal cytotoxicity, highlighting their potential as promising candidates for developing novel therapeutic agents.
Keywords: ADME/Toxicity; Antimicrobial; Coumarin derivatives; Molecular docking; Scratch wound assay; Synthesis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




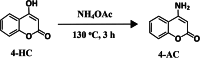

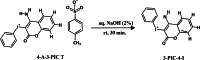

References
-
- Balendres, M. A. O. Plant diseases caused by fungi in the Philippines. Mycol. Trop. Updat Philipp Fungi. 163–188. 10.1016/B978-0-323-99489-7.00014-7 (2022).
-
- Gogoi, D., Baruah, P. J. & Narain, K. Immunopathology of emerging and re-emerging viral infections: An updated overview. Acta Virol.68, 1–7 (2024). - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

