Immunogenicity and safety of CoronaVac vaccine in children and adolescents (Immunita-002, Brazil): A phase IV six-month follow up
- PMID: 40595400
- PMCID: PMC12215048
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-94596-9
Immunogenicity and safety of CoronaVac vaccine in children and adolescents (Immunita-002, Brazil): A phase IV six-month follow up
Abstract
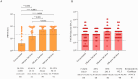
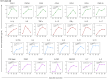
Vaccines are essential for the prevention and control of several diseases, and monitoring the immune response generated by vaccines is crucial. The immune response generated by vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 in children and adolescents is not well defined in terms of the intensity and medium to long-term duration of protective immunity, which may indicate the need for booster doses and could support decisions in public health. The study aims to evaluate the immunogenicity and safety of an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine (CoronaVac) in a two-dose primary protocol in children and adolescents aged 3 to 17 years old in Brazil. Participants were invited to the research at two public healthcare centers located in Serrana (São Paulo) and Belo Horizonte (Minas Gerais), Brazil. They underwent medical interviews to gather their medical history, including COVID-19 history and medical records. Physical exams were conducted, which included measurements of weight, blood pressure, temperature, and pulse rate. Blood samples were obtained from the participants before vaccination, 1 month after the first dose, and at 1, 3, and 6 months after the second dose. These samples were followed up using a virtual platform to monitor post-vaccination reactions and symptoms of COVID-19. The SARS-CoV-2 genome from swab samples of COVID-19 positive individuals was sequenced using NGS. Total antibodies were measured by ELISA, and neutralizing antibodies to the B.1 lineage and Omicron variant (BA.1) were quantified by PRNT and VNT assays. The cellular immune response was evaluated by flow cytometry through the quantification of systemic soluble immune mediators. The follow-up of 640 participants showed that CoronaVac was able to significantly induce the production of total IgG antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 and the production of neutralizing antibodies to the B.1 lineage and Omicron variant. Additionally, a robust cellular immune response was observed, characterized by a wide release of pro-inflammatory and regulatory mediators in the early post-immunization moments. Adverse events recorded so far have been mild and transient, except for seven serious adverse events reported on VigiMed. The results indicate a robust and sustained immune response induced by CoronaVac in children and adolescents for up to six months, providing evidence to support the safety and immunogenicity of this effective immunizer.
Keywords: Antibodies kinetics; COVID-19; Cellular markers; CoronaVac; Neutralizing antibodies; SARS-CoV-2; Vaccine.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






Update of
-
Immunogenicity and safety of inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine (CoronaVac) using two-dose primary protocol in children and adolescents (Immunita-002, Brazil): A phase IV six-month follow up.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Feb 29:rs.3.rs-3931021. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3931021/v1. Res Sq. 2024. Update in: Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 2;15(1):23040. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-94596-9. PMID: 38464059 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- Research Fellow/Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico
- Scholarship/Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de Minas Gerais
- Scholarships/Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico
- U01AI151807/The Coordinating Research on Emerging Arboviral Threats Encompassing the Neotropics (CREATE-NEO), National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- U01 AI151807/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 405786/2022-0/INCT Viral Genomic Surveillance and One Health grant
- Financial support/Instituto Butantan
- Financial support and scholarships/Fundação Oswaldo Cruz
- 465425/2014-3/INCT Dengue Program grant
- Financial support/Parliamentary Amendment
- 2022/03645-1/Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

