Arginine regulates the mucoid phenotype of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae
- PMID: 40595687
- PMCID: PMC12219000
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-61047-y
Arginine regulates the mucoid phenotype of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae
Abstract
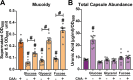
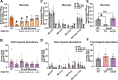
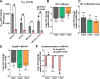
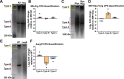
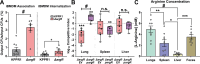
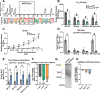
Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae causes severe community-acquired infections, with its mucoid phenotype resulting from altered capsular polysaccharide chain length. While both environmental and genetic factors influence mucoidy, the cues regulating it remain unclear. Here, we show that casamino acids enhance mucoidy without affecting total capsular polysaccharide levels. We show that arginine is both necessary and sufficient in stimulating mucoid expression, activating the rmpADC promoter and increasing rmpADC transcript levels. The arginine regulator, ArgR, is crucial in this process; deleting argR reduces mucoidy and increases capsule chain length diversity. ArgR directly regulates the rmpADC promoter by binding to the ARG box. Loss of argR in vitro increases macrophage association and reduces competitive fitness in lungs, suggesting that ArgR influences adherence and fitness in the lung. Arginine-dependent regulation of mucoidy is conserved in hypervirulent K. pneumoniae isolates, suggesting that this regulatory mechanism broadly controls bacterial cell surface adaptations.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Update of
-
Arginine Regulates the Mucoid Phenotype of Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Nov 20:2024.11.20.624485. doi: 10.1101/2024.11.20.624485. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nat Commun. 2025 Jul 1;16(1):5875. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-61047-y. PMID: 39605402 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Lan, P., Jiang, Y., Zhou, J. & Yu, Y. A global perspective on the convergence of hypervirulence and carbapenem resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist.25, 26–34 (2021). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K99 AI175481/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM150588/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R35GM150588/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- K22 AI145849/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K99A1175481/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

