Aerobic exercise-induced changes in fluid biomarkers in Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 40595707
- PMCID: PMC12215721
- DOI: 10.1038/s41531-025-01042-8
Aerobic exercise-induced changes in fluid biomarkers in Parkinson's disease
Abstract
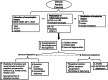
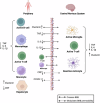
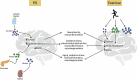
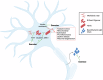
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disease characterized by motor and non-motor symptoms that progressively deteriorate and for which there is no disease-modifying pharmacological treatment. Exercise is widely recommended for individuals with PD due to its potential neuroprotective benefits. However, the mechanisms underlying these exercise-induced effects in PD remain poorly understood. Analyzing fluid biomarkers responsive to exercise could offer valuable insights into the mechanisms by which exercise impacts PD and aid in optimizing exercise prescriptions for individuals with PD. This review explores exercise-responsive biomarkers categorized into three key groups-neurotrophic, inflammatory, and neuroendocrine markers. It highlights both well-validated biomarkers and candidates with promising potential. We also highlight key biomarkers linked to PD pathology, such as α-synuclein, and their potential connection to exercise based on current evidence. Comprehensive characterization of these biomarkers will advance our understanding of the biological effects of exercise in PD, enabling mechanism-based and objective measures to evaluate exercise response in future clinical trials and its impact on PD signs and symptoms.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Hirtz, D. et al. How common are the “common” neurologic disorders?. Neurology68, 326–337 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Dorsey, E. R. & Bloem, B. R. The Parkinson Pandemic-A Call to Action. JAMA Neurol.75, 9–10 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Kalia, L. V. & Lang, A. E. Parkinson’s disease. Lancet386, 896–912 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Vijiaratnam, N., Simuni, T., Bandmann, O., Morris, H. R. & Foltynie, T. Progress towards therapies for disease modification in Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol.20, 559–572 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Lang, A. E. & Espay, A. J. Disease Modification in Parkinson’s Disease: Current Approaches, Challenges, and Future Considerations. Mov. Disord.33, 660–677 (2018). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
- T32-HD07418/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD)
- U01 NS113851/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K23NS123506/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)
- U01NS113851/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)
- T32 HD101395/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- K23 NS123506/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001422/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- T32-HD101395/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD)
- T32 HD007418/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR001422/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

