Exploring the interconnected properties of cannabidiol suspensions and orodispersible films
- PMID: 40595713
- PMCID: PMC12215374
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-02859-2
Exploring the interconnected properties of cannabidiol suspensions and orodispersible films
Abstract
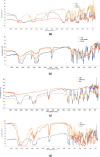
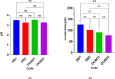
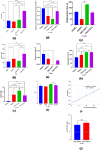
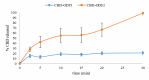
In this study, orodispersible films (ODFs) were developed as fast-releasing formulations for pediatric patients suffering from Lennox-Gastaut or Dravet syndrome, with cannabidiol (CBD) selected as the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API). The properties of the ODFs were evaluated both before and after casting, with a focus on establishing a correlation between the properties of colloidal dispersion/suspension and ODFs to enhance understanding of the manufacturing process. Two blank colloidal dispersions were characterized for spreadability, viscosity, tangential stress, and pH, and their properties were correlated with those of blank ODFs, including mass uniformity, thickness, folding endurance, thickness-normalized crushing strength, disintegration time (evaluated through two different methods) and adhesivity. The strength and direction of the correlation were established via the Pearson coefficient. The same statistical approach was applied to assess correlation between CBD suspension (DCBD1, DCBD2) properties and CBD-ODF parameters. For the suspensions, particle size evaluation was also considered. Although few statistically significant positive or negative correlations were observed, a notable finding of this study was the dissolution behavior of CBD-ODF2, where nearly 100% of the API was released at 30 min, which is consistent with the disintegration behavior evaluated through the pharmacopeial method. Notably, CBD is classified as a Biopharmaceutical Classification System (BCS) Class II compound.
Keywords: Colloidal dispersions; Correlation coefficients; Dissolution behavior; Polymeric films.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Consent for publication: All the authors consent to this final form for publication.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comparative efficacy and safety of stiripentol, cannabidiol and fenfluramine as first-line add-on therapies for seizures in Dravet syndrome: A network meta-analysis.Epilepsia Open. 2024 Apr;9(2):689-703. doi: 10.1002/epi4.12923. Epub 2024 Mar 1. Epilepsia Open. 2024. PMID: 38427284 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of cannabidiol oral bioavailability through the development of nanostructured lipid carriers: In vitro and in vivo evaluation studies.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2025 Aug;15(8):2722-2732. doi: 10.1007/s13346-024-01766-9. Epub 2024 Dec 30. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2025. PMID: 39738884 Free PMC article.
-
An open-label phase I comparator-controlled clinical trial to assess tolerability and pharmacokinetics of IHL-675 A a fixed dose combination of cannabidiol plus hydroxychloroquine in healthy volunteers.Sci Rep. 2025 Jun 3;15(1):19357. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-04573-5. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40456820 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Intravenous magnesium sulphate and sotalol for prevention of atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass surgery: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2008 Jun;12(28):iii-iv, ix-95. doi: 10.3310/hta12280. Health Technol Assess. 2008. PMID: 18547499
-
Native and pregelatinized starches of bitter yam as film formers for oral dissolving formulations.Polim Med. 2025 Jan-Jun;55(1):7-19. doi: 10.17219/pim/202946. Polim Med. 2025. PMID: 40599102
References
-
- Galande, A. D., Khurana, N. A. & Mutalik, S. Pediatric dosage forms-challenges and recent developments: A critical review. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci.10, 155–166. 10.7324/JAPS.2020.10718 (2020).
-
- Wadher, K., Dhote, K., Mane, M., Khapne, A. & Umekar, A. G. M. Orodispersible dosage form: advancement and challenges (SJS). Int. J. Pharm. Res. Heal Sci.7, 3013–3019. 10.21276/ijprhs.2019.04.01 (2019).
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 164/27/10.01.2023/"George Emil Palade" University of Medicine, Pharmacy, Science and Technology of Târgu Mureș, Romania
- 164/27/10.01.2023/"George Emil Palade" University of Medicine, Pharmacy, Science and Technology of Târgu Mureș, Romania
- 164/27/10.01.2023/"George Emil Palade" University of Medicine, Pharmacy, Science and Technology of Târgu Mureș, Romania
- 164/27/10.01.2023/"George Emil Palade" University of Medicine, Pharmacy, Science and Technology of Târgu Mureș, Romania
- 164/27/10.01.2023/"George Emil Palade" University of Medicine, Pharmacy, Science and Technology of Târgu Mureș, Romania
- 164/27/10.01.2023/"George Emil Palade" University of Medicine, Pharmacy, Science and Technology of Târgu Mureș, Romania
- 164/27/10.01.2023/"George Emil Palade" University of Medicine, Pharmacy, Science and Technology of Târgu Mureș, Romania
- 164/27/10.01.2023/"George Emil Palade" University of Medicine, Pharmacy, Science and Technology of Târgu Mureș, Romania
- 164/27/10.01.2023/"George Emil Palade" University of Medicine, Pharmacy, Science and Technology of Târgu Mureș, Romania
- 164/27/10.01.2023/"George Emil Palade" University of Medicine, Pharmacy, Science and Technology of Târgu Mureș, Romania
- 164/27/10.01.2023/"George Emil Palade" University of Medicine, Pharmacy, Science and Technology of Târgu Mureș, Romania
- 164/27/10.01.2023/"George Emil Palade" University of Medicine, Pharmacy, Science and Technology of Târgu Mureș, Romania
- 164/27/10.01.2023/"George Emil Palade" University of Medicine, Pharmacy, Science and Technology of Târgu Mureș, Romania
- 164/27/10.01.2023/"George Emil Palade" University of Medicine, Pharmacy, Science and Technology of Târgu Mureș, Romania
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

