Graduate students and supervisors matching decision-making considering stability-based fairness based on TOPSIS and grey correlation degrees
- PMID: 40595721
- PMCID: PMC12214553
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-00388-6
Graduate students and supervisors matching decision-making considering stability-based fairness based on TOPSIS and grey correlation degrees
Abstract
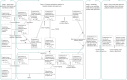
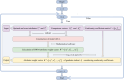
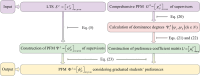
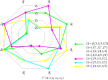
In view of the lack of research on graduate students and supervisors matching (GSSM) decision-making, this study proposes a novel many-to-one matching decision-making method for graduate students and supervisors (GSS) considering conformity psychology and graduate students' preferences from a stability-based fairness perspective. First, the many-to-one matching problem for GSS is described. To tackle this problem, linguistic term matrices (LTMs) provided by bilateral subjects are transformed into Pythagorean fuzzy matrices (PFMs). On the one hand, according to the transference relation of graduate students, a conformity coefficient matrix is built. Then a PFM considering conformity psychology is established. Attribute weight vectors adjusted by conformity coefficients are formulated based on comparison information of graduate students and the conformity coefficient matrix. On this basis, a comprehensive PFM of graduate students is constructed. On the other hand, a preference coefficient matrix of graduate students is built by using TODIM (a Portuguese acronym for interactive and multicriteria decision making). And a PFM considering graduate students' preferences is constructed. Attribute weight vectors of supervisors are determined based on attribute comparison information. On this basis, a comprehensive PFM of supervisors is set up. Furthermore, satisfaction matrices of GSS are constructed by using TOPSIS (technique for order preference by similarity to the ideal solution) and grey correlation degrees. A many-to-one GSSM model considering stability-based fairness is established by introducing matching matrix and stable matching matrix. The many-to-one matching model is then transformed into a one-to-one matching model by introducing virtual supervisor subjects; the optimal matching scheme between GSS is obtained by solving the above model. Finally, the feasibility, effectiveness and innovation of the proposed method are verified by an example analysis. The key findings of this study are listed as follows: (1) A new score of Pythagorean fuzzy numbers (PFNs) is proposed. (2) A method for converting linguistic term sets (LTSs) into PFNs is developed. (3) A weight calculation that combines conformity psychology with BWM is improved. (4) A novel method for satisfaction calculation considering conformity psychology and graduate students' preferences is introduced. (5) A GSSM model considering stability-based fairness is built.
Keywords: Conformity psychology; Graduate students and supervisors matching decision-making; Many-to-one matching; Pythagorean fuzzy environment; Stability-based fairness.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures












Similar articles
-
A novel MCDM method for assessing student employability psychology using complex Pythagorean hesitant fuzzy Sugeno Weber aggregation.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 22;15(1):26676. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-10579-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40695861 Free PMC article.
-
Patient-doctor communication.Med Clin North Am. 2003 Sep;87(5):1115-45. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(03)00066-x. Med Clin North Am. 2003. PMID: 14621334
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
A decision-theoretic framework for wastewater treatment performance assessment based on a fuzzy parameterized fuzzy hypersoft set approach.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):20706. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-07896-5. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40596323 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
References
-
- Su, W., Zhang, Y., Yin, Y. & Dong, X. The influence of teacher-student relationship on innovative behavior of graduate student: The role of proactive personality and creative self-efficacy. Think. Skills Creat.52, 101529 (2024).
-
- Zhang, H., Liu, Y., Selang, D. & He, Y. A. Three-way decision with prospect-regret theory under Pythagorean fuzzy environments. Appl. Soft Comput.167, 112286 (2024).
-
- Zhang, Y., Jian, J. & Yuan, Y. How supervisors’ academic capital influences business graduate students’ perceived supervisor support and creativity, Evidence from the tutorial system in China. Int. J. Manag. Educ.20(3), 100732 (2022).
-
- Ma, X., Qin, J., Martínez, L. & Pedrycz, W. A linguistic information granulation model based on best-worst method in decision making problems. Inf. Fus.89, 210–227 (2023).
-
- Seikh, M. R. & Chatterjee, P. Evaluation and selection of E-learning websites using intuitionistic fuzzy confidence level based Dombi aggregation operators with unknown weight information. Appl. Soft Comput.163, 111850 (2024).
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

