The effects of non-nutritive sweeteners on lipid profile in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials
- PMID: 40595722
- PMCID: PMC12217003
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-00612-3
The effects of non-nutritive sweeteners on lipid profile in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials
Abstract
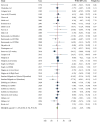
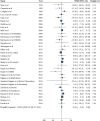
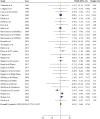
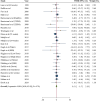
Non-nutritive sweeteners (NNS) have been suggested as a viable solution to reduce sugar consumption. However, conflicting and uncertain evidence regarding their impact on lipid profile exists. This meta-analysis assesses the effects of different types of NNS on lipid profile markers. PubMed, Web of Science ISI, Scopus, and Google Scholar were searched for relevant articles up to September 2024. The Cochrane Collaboration tool was used for the quality assessment, and the evidence's trustworthiness was assessed using the Grading of Assessment, Development, and Evaluation of Recommendations (GRADE). A total of 28 articles revealed that NNS might not have a significant effect on serum triglycerides (Weighted mean difference (WMD): -2.66, 95% confidence interval (CI): -6.29, 0.98 mg/dL, n = 2209, level of confidence: low), total cholesterol (WMD: -0.44, 95% CI: -2.96, 2.08 mg/dl, n = 2047, level of confidence: low), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (WMD: 0.03, 95% CI: -0.68, 0.74 mg/dl, n = 2097, level of confidence: low), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (WMD: 0.51, 95% CI: -1.57, 2.59 mg/dl, n = 1777, level of confidence: low) and very low-density lipoprotein (WMD: 2.20, 95% CI: -2.66, 7.06 mg/dl, n = 154, level of confidence: very low). It is demonstrated that NNS might not affect serum lipid profile.
Keywords: Artificial sweeteners; High-density lipoprotein; Low-density lipoprotein; Total cholesterol; Triglyceride; Very low-density lipoprotein.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
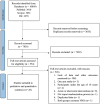
Similar articles
-
Effects of sumac supplementation on lipid profile: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Phytother Res. 2024 Jan;38(1):241-252. doi: 10.1002/ptr.8046. Epub 2023 Oct 21. Phytother Res. 2024. PMID: 37864474
-
Effects of green tea on lipid profile in overweight and obese women.Int J Vitam Nutr Res. 2024 Jun;94(3-4):239-251. doi: 10.1024/0300-9831/a000783. Epub 2023 Apr 21. Int J Vitam Nutr Res. 2024. PMID: 37082776
-
Comprehensive meta-analysis of the effects of oral medroxyprogesterone acetate plus conjugated equine oestrogens on the lipid profile in women: Insights from randomized controlled trials.Eur J Clin Invest. 2024 Aug;54(8):e14211. doi: 10.1111/eci.14211. Epub 2024 May 10. Eur J Clin Invest. 2024. PMID: 38726889
-
The effects of Garcinia cambogia (hydroxycitric acid) on lipid profile: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Phytother Res. 2024 Feb;38(2):1028-1043. doi: 10.1002/ptr.8102. Epub 2023 Dec 27. Phytother Res. 2024. PMID: 38151892
-
The effect of tamoxifen on the lipid profile in women: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Exp Gerontol. 2022 Mar;159:111680. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2021.111680. Epub 2021 Dec 30. Exp Gerontol. 2022. PMID: 34973347
References
-
- Cooney, M. et al. HDL cholesterol protects against cardiovascular disease in both genders, at all ages and at all levels of risk. Atherosclerosis206, 611–616 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Mendis, S., Puska, P., Norrving, B. & Organization, W. H. Global Atlas on Cardiovascular Disease Prevention and Control (World Health Organization, 2011).
-
- Bamba, V. & Rader, D. J. Obesity and atherogenic dyslipidemia. Gastroenterology132, 2181–2190. 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.03.056 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Djelilovic-Vranic, J. et al. Predilection role diabetes mellitus and dyslipidemia in the onset of ischemic stroke. Med. Archives. 67, 120 (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

