Modulating immune-stem cell crosstalk enables robust bone regeneration via tuning compositions of macroporous scaffolds
- PMID: 40595820
- PMCID: PMC12219738
- DOI: 10.1038/s41536-025-00421-2
Modulating immune-stem cell crosstalk enables robust bone regeneration via tuning compositions of macroporous scaffolds
Abstract
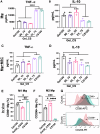
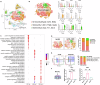
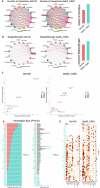
Following bone injury, macrophages (Mφ) initiate the immune response by secreting signals that recruit mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) and other niche cells to shape healing. Despite its importance, the potential of enhancing bone regeneration by modulating immune-stem cell crosstalk is largely unexplored. Here, we report a macroporous microribbon (µRB) scaffold with tunable ratios of gelatin (Gel) and chondroitin sulfate (CS), achieving rapid endogenous bone regeneration in a critical-sized defect model without exogenous growth factors or cells. The 3D MSC/Mφ co-culture model, but not the mono-culture model, effectively identified Gel50_CS50 as the leading ratio for accelerating bone regeneration in vivo. Single-cell sequencing (scRNAseq) and CellChat analysis revealed that Gel50_CS50 significantly enhanced the cellular crosstalk among Mφ and other bone niche cell types, with signaling pathways linked to anti-inflammation, angiogenesis, and osteogenesis. This study demonstrates Gel50_CS50 µRB as a promising biomaterial-based therapy for treating critical-sized bone defects by modulating cellular crosstalk.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

