Effects of sport disciplines on offspring sex ratio in elite athletes: an observational study
- PMID: 40595831
- PMCID: PMC12217473
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-05445-8
Effects of sport disciplines on offspring sex ratio in elite athletes: an observational study
Abstract
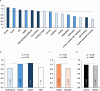
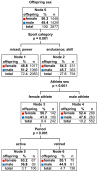
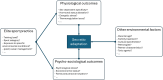
The sex ratio (SR; the ratio of male to female births) is a demographic indicator close to 1.04 in the worldwide population that can variate depending in several environmental conditions. The practice of elite sport exposes athletes to several factors known to impact SR, in particular high physiological (training loads) and psychological (management of personal and professional life) levels of stress. However, knowledge about the effect of elite sport practice on SR is limited. We used binomial logistic regression to analyze the SR of the offspring (n = 2995 births) of 2132 athletes (18.7% of females) from various sports including 1597 athletes selected in their national team. We showed that endurance elite athletes are more likely to have daughters compared to athletes from mixed or power-oriented disciplines. Furthermore, classification tree analysis revealed that the probability of siring daughters was strongly enhanced in female athletes who gave birth during their professional sport career (SR = 0.581). Our results highlight the practice of elite sport as a condition associated with specific adaptation of the reproductive system. This raises questions about the mechanisms responsible for SR alteration (ranging from physiological to socio-economic aspects), opening new avenues in sports sciences and in reproductive biology.
Keywords: Elite sport; Gender inequality; Human reproduction; Sex-ratio.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Catalano, R., Bruckner, T., Gould, J., Eskenazi, B. & Anderson, E. Sex ratios in California following the terrorist attacks of September 11, 2001. Hum. Reprod.20, 1221–1227 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

