Development and evaluation of cepharanthine-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex oral tablets for prevention and treatment of COVID-19 lung injury
- PMID: 40595876
- PMCID: PMC12215774
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-04167-1
Development and evaluation of cepharanthine-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex oral tablets for prevention and treatment of COVID-19 lung injury
Abstract
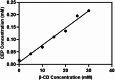
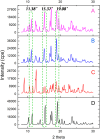
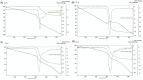
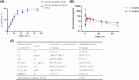
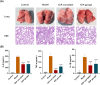
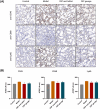
The symptoms of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) range from severe lung disease to milder manifestations, such as cough and throat irritation. As a bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloid, cepharanthine (CEP) has various pharmacological properties, such as antifibrotic, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antiviral effects. However, its poor solubility and low bioavailability hinder subsequent drug development. Inclusion complex technology is a well-established drug delivery method that improves drug bioavailability. Therefore, in our study, we encapsulated CEP with β-cyclodextrin and formulated it into oral tablets. Oral tablets can be absorbed through sublingual and buccal mucosa, improving CEP bioavailability, facilitating convenient dosing, and thereby enhancing its therapeutic efficacy. The cepharanthine-β-cyclodextrin (CEP-β-CD) inclusion complex was prepared using the co-grinding method. It was characterized using scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and differential scanning calorimetry to assess its physicochemical properties. Subsequently, the quality of the CEP-β-CD oral tablets was evaluated according to the relevant requirements of the 2020 edition of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia. Furthermore, the pharmacokinetic characteristics of the oral tablets were assessed in beagles. Finally, the anti-inflammatory effects of the CEP-β-CD oral tablets were evaluated in alveolar macrophage MH-S cells and a mouse pneumonia model. Our results suggest that the formulation of the CEP-β-CD inclusion complex into oral tablets is a promising preventive and therapeutic approach for lung injury caused by COVID-19.
Keywords: Anti-inflammatory; Cepharanthine; Inclusion complex; Oral tablet.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical approval: The animal study protocol was approved by the Institution of Animal Care and Use Committee, Academy of Military Medical Science (IACUC-DWZX-2024-P626, Beijing, China). All animal experiments were complied with the ARRIVE guidelines, and were carried out in accordance with the U.S. Public Health Service Policy on Humane Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.
Figures




References
-
- Dl, G. How to understand the overlap of long COVID, chronic fatigue syndrome/myalgic encephalomyelitis, fibromyalgia and irritable bowel syndromes. Semin. Arthritis Rheum.67 (2024). - PubMed
-
- Adjaye-Gbewonyo, D., Vahratian, A., Perrine, C. G. & Bertolli, J. Long COVID in adults: united States, 2022. NCHS Data Brief 1–8 (2023). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- No. 20SWAQK22/Natural Science Foundation of Beijing Municipality
- No. 20SWAQK22/Natural Science Foundation of Beijing Municipality
- No. 20SWAQK22/Natural Science Foundation of Beijing Municipality
- No. 20SWAQK22/Natural Science Foundation of Beijing Municipality
- No. 20SWAQK22/Natural Science Foundation of Beijing Municipality
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

