A deep learning model for diagnosis of inherited retinal diseases
- PMID: 40595896
- PMCID: PMC12214717
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-04648-3
A deep learning model for diagnosis of inherited retinal diseases
Abstract
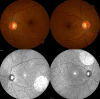
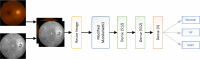
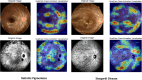
To evaluate the performance of a multi-input deep learning (DL) model in detecting two common inherited retinal diseases (IRDs), i.e. retinitis pigmentosa (RP) and Stargardt disease (STGD), and differentiating them from healthy eyes. This cross-sectional study includes 391 cases, consisting of 158 subjects with RP, 62 patients with STGD, and 171 healthy individuals. The image dataset is publicly available at http://en.riovs.sbmu.ac.ir/Access-to-Inherited-Retinal-Diseases-Image-Bank . Separate networks using the same hyperparameters were trained and tested on the dataset. Two single-input MobileNetV2 networks were employed for color fundus photography (CFP) and infrared (IR) images, and a multi-input MobileNetV2 network was applied using both imaging modalities simultaneously. The single-input MobileNetV2 achieved 94.44% diagnostic accuracy using CFP, and 94.44% accuracy employing IR images, respectively. The multi-input MobileNetV2 network outperformed both single-input networks with an accuracy of 96.3%. The impact of single-input and multi-input architectures was further evaluated on state-of-the-art neural network models and machine learning algorithms. The deep learning networks utilized in this study achieved high performance for detection of IRDs. Application of a multi-input network employing both CFP and IR image inputs improves the overall performance of the model and its diagnostic accuracy.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Deep learning architectures; Inherited retinal diseases; Machine learning algorithms; Retinitis pigmentosa; Stargardt disease.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A deep learning approach to direct immunofluorescence pattern recognition in autoimmune bullous diseases.Br J Dermatol. 2024 Jul 16;191(2):261-266. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljae142. Br J Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38581445
-
Deep learning detects retropharyngeal edema on MRI in patients with acute neck infections.Eur Radiol Exp. 2025 Jun 19;9(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s41747-025-00599-6. Eur Radiol Exp. 2025. PMID: 40536731 Free PMC article.
-
A novel deep learning framework for retinal disease detection leveraging contextual and local features cues from retinal images.Med Biol Eng Comput. 2025 Jul;63(7):2029-2046. doi: 10.1007/s11517-025-03314-0. Epub 2025 Feb 7. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2025. PMID: 39918766
-
Stem cell therapy for inherited retinal diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023 Oct 5;14(1):286. doi: 10.1186/s13287-023-03526-x. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 37798796 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence for detecting keratoconus.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Nov 15;11(11):CD014911. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014911.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37965960 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

