Surface keratin 1, a tumor-selective peptide target in human triple-negative breast cancer
- PMID: 40595898
- PMCID: PMC12216204
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-05351-z
Surface keratin 1, a tumor-selective peptide target in human triple-negative breast cancer
Abstract
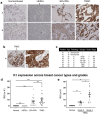
Targeting drugs to cancer cells via overexpressed cell-surface receptors has emerged as an effective therapeutic strategy for several cancers. However, identifying cell-surface receptors that allow selective uptake of targeting ligands by cancer cells-while sparing normal cells-remains a challenge, especially for triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), which lacks a well-defined receptor for targeted delivery. In this study, immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis revealed that human TNBC patient tissues have significantly higher levels of keratin 1 (K1) compared to normal breast tissues. Among TNBC tissues, grade 3 tumors showed significantly higher (threefold) K1 expression compared to grade 2 tumors. We analyzed human TNBC and normal mammary epithelial cells to detect K1 from cell lysates using three methods: mass spectrometry, peptide mass fingerprinting, and Western blot. TNBC cell lysates confirmed the presence and high expression levels of 67 kDa K1. Importantly, intact cells showed that K1 is uniformly present on the surface of TNBC cells, while no or minimal cell-surface K1 was found in normal mammary epithelial cells using immunofluorescence confocal microscopy. Further, we show that cell-surface K1 was utilized by TNBC-selective peptide 18-4 for its uptake via cell-surface receptor (K1)-mediated endocytosis in TNBC cells, and the presence of peptide 18-4 did not affect the assembly of endogenous cytoplasmic K1. Taken together, our results demonstrate that K1 is overexpressed in human TNBC, and cell-surface K1 represents a promising new target for directed delivery in TNBC using targeting ligands such as peptide 18-4.
Keywords: Cell-surface keratin 1; Keratin 1 expression; TNBC; Targeted drug delivery; Tumor-selective peptide.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical approval: The patient tissue samples used in this study were purchased from TissueArray.com. All ethical considerations were followed when using human tissue samples.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Targeted delivery of DAPT using dual antibody functionalized solid lipid nanoparticles for enhanced anti-tumour activity against triple negative breast cancer.Int J Pharm. 2025 Feb 10;670:125142. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2024.125142. Epub 2024 Dec 31. Int J Pharm. 2025. PMID: 39746584
-
Inhibition of Interleukin-8/C-X-C Chemokine Receptor 2 Signaling Axis Prevents Tumor Growth and Metastasis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells.Pharmacology. 2025;110(3):178-190. doi: 10.1159/000545659. Epub 2025 Apr 4. Pharmacology. 2025. PMID: 40188812 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Single-cell ligand-receptor profiling reveals an immunotherapy-responsive subtype and prognostic signature in triple-negative breast cancer.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 10;16:1590951. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1590951. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40557143 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of residual disease as a prognostic factor for survival in women with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer after primary surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 26;9(9):CD015048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015048.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36161421 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R03AR076484/National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases of the National Institutes of Health
- R15 CA208656/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR079428/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R03 AR076484/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R15CA208656/National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

