Gluconeogenesis related gene signatures as biomarkers for nonspecific orbital inflammation
- PMID: 40595959
- PMCID: PMC12219558
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-05002-3
Gluconeogenesis related gene signatures as biomarkers for nonspecific orbital inflammation
Abstract
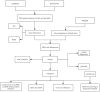
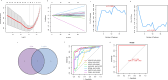
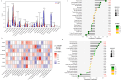
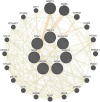
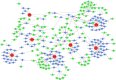
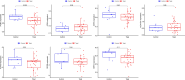
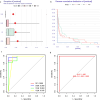
Nonspecific orbital inflammation (NSOI) is a chronic, idiopathic inflammatory disorder marked by persistent tissue proliferation and immune activation. Gluconeogenesis, a core metabolic pathway enabling endogenous glucose production in the absence of dietary input, plays a vital role in cellular energy homeostasis and immune regulation. Metabolic rewiring of immune cells is not merely a consequence of inflammation but a critical determinant of disease trajectory in orbital disorders. Within this conceptual landscape, the exploration of gluconeogenesis represents a logical and timely extension, offering potential insights into how alternative metabolic pathways may orchestrate immune cell function and fibrotic responses in the orbital microenvironment. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were intersected with a curated list of 53 gluconeogenesis-related genes (GRGs) to pinpoint candidates potentially involved in NSOI. Advanced methodologies, including Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) and Gene Set Variation Analysis (GSVA), were employed to elucidate biological functions. Further refinement using Lasso regression and Support Vector Machine-Recursive Feature Elimination (SVM-RFE) facilitated the identification of key hub genes and evaluated their diagnostic potential for NSOI. Our investigation identified seven GRGs, ADH5, BPGM, PGM1, ADH4, ADH1B, G6PC3, ALDH1B1, that are closely associated with NSOI. Functional analyses revealed their involvement in processes such as pyruvate metabolic process, hexose metabolic process, monosaccharide metabolic process. Notably, the diagnostic capabilities of these GRGs demonstrated significant efficacy in distinguishing NSOI from unaffected states. Through rigorous bioinformatics analyses, this study identifies ADH5, BPGM, PGM1, ADH4, ADH1B, G6PC3, ALDH1B1 as novel biomarker candidates for NSOI, shedding light on their potential roles in the disease's pathogenesis.
Keywords: Biomarker candidates; Cell communication; Gluconeogenesis-related gene; Immune infiltration; Nonspecific orbital inflammation.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This manuscript is not a clinical trial, hence the ethics approval and consent to participation are not applicable. Consent for publication: All authors have read and approved this manuscript to be considered for publication.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Immune Regulation and ECM-Related Pathway Enrichment Reveal ATP2A3 as a Prognostic Biomarker for Nonspecific Orbital Inflammation: An Integrated Machine Learning and Mendelian Randomization Analysis.Mediators Inflamm. 2025 Jun 13;2025:7061507. doi: 10.1155/mi/7061507. eCollection 2025. Mediators Inflamm. 2025. PMID: 40548296 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated multiple machine learning and Mendelian randomization reveal LTF gene as a prognostic biomarker for nonspecific orbital inflammation.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2025 Aug 4;26(1):143. doi: 10.1186/s40360-025-00980-6. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40760708 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatic validation and machine learning-based exploration of purine metabolism-related gene signatures in the context of immunotherapeutic strategies for nonspecific orbital inflammation.Front Immunol. 2024 Mar 28;15:1318316. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1318316. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38605967 Free PMC article.
-
How lived experiences of illness trajectories, burdens of treatment, and social inequalities shape service user and caregiver participation in health and social care: a theory-informed qualitative evidence synthesis.Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2025 Jun;13(24):1-120. doi: 10.3310/HGTQ8159. Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2025. PMID: 40548558
-
Factors that influence parents' and informal caregivers' views and practices regarding routine childhood vaccination: a qualitative evidence synthesis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Oct 27;10(10):CD013265. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013265.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34706066 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Braich, P. S., Kuriakose, R. K., Khokhar, N. S., Donaldson, J. C. & McCulley, T. J. Factors associated with multiple recurrences of nonspecific orbital inflammation aka orbital pseudotumor. Int. Ophthalmol.38(4), 1485–1495 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Zhang, X. C. et al. Man with a swollen eye: Nonspecific orbital inflammation in an adult in the emergency department. J. Emerg. Med.55(1), 110–113 (2018). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

