Rice QTL hotspots related with seed grain size, shape, weight, and color based on genome wide association study and linkage mapping
- PMID: 40595972
- PMCID: PMC12218392
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-05814-3
Rice QTL hotspots related with seed grain size, shape, weight, and color based on genome wide association study and linkage mapping
Abstract
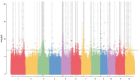
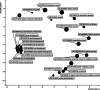
Rice is a staple crop worldwide, with seed traits such as size, shape, weight, and color playing crucial roles in agricultural productivity and consumer preferences. Despite significant progress, the genetic basis underlying the variation in hulled and unhulled seed grain traits remains partially unexplored. This study presents a comprehensive analysis combining GWAS and QTL mapping to dissect the genetic architecture of hulled and unhulled seed characteristics in rice. The aim is to identify quantitative trait loci (QTLs) associated with these traits using an integration of multi-model approach genome-wide association studies (GWAS) and linkage mapping analysis. The study analyzed 244 local rice varieties for GWAS and 90 Recombinant Inbred Lines for linkage mapping analysis. The traits observed included hulled and unhulled seed grain area, perimeter, length, width, length-to-width ratio, circularity, weight, and color (RGB, HSV, Lab, yCbCr). A total of 23 QTL regions were identified, with two major QTL hotspots located on chromosomes 7 and 2. Specifically, QTL hotspots on chromosome 7 were associated with grain size, shape, and weight, while those on chromosome 2 were linked to seed color. A total of 530 SNPs significantly associated with the traits were distributed across 12 rice chromosomes, corroborating the QTL hotspot regions. Six genes on chromosome 7 and seven genes on chromosome 2 were proposed as candidate genes regulating seed grain traits. These findings provide valuable insights into the genetic control of rice seed traits and offer potential targets for breeding programs aimed at improving rice quality and yield.
Keywords: Genome-wide association study (GWAS); Grain; Hulled seed; Quantitative trait loci (QTL); Rice.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Nayak, A. K. et al. Genetic dissection of grain size traits through genome-wide association study based on genic markers in rice. Rice Sci.29, 462–472 (2022).
-
- Qiu, X. et al. Genome-wide association mapping for grain shape in rice accessions. Int. J. Agric. Biol.23, 582–588 (2020).
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

